AbstractPurposeTo evaluate the efficacy of gemcitabine-based chemotherapy, particularly in patients with anthracycline- and taxane-pretreated 2nd-line or greater metastatic breast cancer, and to compare gemcitabine monotherapy (G) with two gemcitabine-based doublets, gemcitabine/vinorelbine (GV) and gemcitabine/capecitabine (GX).
Materials and MethodsOf 124 consecutive patients who progressed after anthracycline- and taxane-containing chemotherapy, 58 received G alone, 38 received GV, and 28 received GX; their outcomes were analyzed retrospectively.
ResultsThe median number of prior metastatic chemotherapy regimens was 2 (range 0~4). Visceral metastases were observed in 65 patients (51.4%). The overall response rate was 19.3% (21 partial responses). After a median follow-up period of 21.4 months, the overall survival was 7.6 months (95% CI: 5.5~9.6 months) and the median time to progression was 3.1 months (95% CI: 2.0~4.2 months). Compared with monotherapy (G), com - bination therapy with vinorelbine or capecitabine (GV/GX) was associated with a significantly higher response rate (8.2% vs. 28.3%, p=0.008) and a significantly longer median time to progression (2.8 vs. 3.5 months; p=0.028), but overall survival did not differ between the groups (7.4 vs. 8.2 months, respectively; p=0.54). Most of the adverse treatment-related events were mild to moderate in intensity. The most common adverse event was hematologic toxicity. Multivariate analysis showed that poor performance status and a short disease-free interval were independent prognostic factors for impaired overall survival.
ConclusionsThe combination of gemcitabine with vinorelbine or capecitabine was an active and well-tolerated treatment option for taxane- and anthracycline-pretreated 2nd-line or greater metastatic breast cancer patients, and gemcitabine-based doublets were more beneficial than gemcitabine monotherapy in alleviating symptoms for these patients.
INTRODUCTIONDespite advances in breast cancer screening, improved locoregional treatments, and adjuvant systemic therapy, only modest progress has been made in improving survival for women with metastases. The median survival for patients with metastases is 1~2 years and, as a result, the management of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) remains a major clinical challenge (1). Recent changes in therapy regimens have shifted the use of anthracyclines and taxanes to earlier in the course of disease, including during adjuvant/neoadjuvant therapy, and the proportion of patients previously exposed to taxane and anthracycline is increasing in the metastatic setting. However, when patients experience progression following taxane-based chemotherapy, there are few therapeutic options.
Gemcitabine is a nucleoside analogue of deoxycytidine that is enzymatically activated inside the cell where it subsequently inhibits DNA synthesis (2). It is efficacious in metastatic breast cancer, both as a single agent and in various combination regimens (3~6). Gemcitabine monotherapy has produced overall response rates of up to 37% in a first-line setting and 26% in studies limited to second- or third-line therapy after anthracycline and/or taxane exposure; response rates as high as 29% have been reported, and the median time to progression varied from 2 to 6 months (7~11). Moreover, gemcitabine has a favorable toxicity profile, making it suitable for combination therapy. Various combinations of gemcitabine with other effective agent have resulted in high response rates. In metastatic breast cancer, however, there is little compelling evidence that combination chemotherapy is superior to monotherapy. Preferred first-line chemotherapies therefore include sequential single agent or combination chemotherapy (12). It is commonly assumed, however, that combination chemotherapy will result in a superior response rate, as well as improved palliation of symptoms, progression-free and overall survival, in patients with advanced malignancies. To date, there have been no comparisons of gemcitabine-based single and combination therapy regimens in salvage settings.
Therefore, we retrospectively assessed the efficacy of gemcitabine-based chemotherapy and compared gemcitabine monotherapy (G) with gemcitabine-based combination therapies with vinorelbine (GV) or capecitabine (GX) in patients with heavily pre-treated metastatic breast cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODSBetween May 2002 and February 2005, a total of 145 female patients with metastatic breast cancer were treated with gemcitabine-based salvage chemotherapy regimens following anthracycline and taxane treatments at the Asan Medical Center. Inclusion criteria included: 1) histologically documented invasive ductal or lobular carcinoma; 2) prior exposure to both anthracyclines and taxanes; 3) relapse within 1 year of completing adjuvant anthracycline- and taxane-based chemotherapy; 4) at least one measurable or evaluable lesion; and 5) salvage treatment with gemcitabine alone (G) or gemcitabine in combination with vinorelbine (GV) or capecitabine (GX).
Of the 145 patients, 124 patients fulfilled these eligibility criteria and were enrolled in the study. Patient information and tumor-specific characteristics were obtained from surgical, pathological and oncological records. The Institutional Review Board of the Asan Medical Center approved the protocol of this retrospective study.
1) Treatment scheduleIn group G, gemcitabine was administered at 1,000 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15 every 4 weeks; group GV received gemcitabine at 1,000 mg/m2 and vinorelbine at 25 mg/m2 on days 1 and 8 every 3 weeks; and in group GX, gemcitabine was given at 1,000 mg/m2 on days 1 and 8 (D1, D8) every 3 weeks and capecitabine was administered at 1,000 mg/m2 using the standard intermittent schedule (2 weeks of treatment followed by a 1-week rest period). In cases of grade 3/4 hematologic or non-hematologic toxicities, doses were adjusted based on leukocyte and platelet counts on the day of treatment or on clinical assessments of non-hematologic toxicities, respectively.
2) Response evaluation and toxicity assessmentPatients with measurable disease were assessed for response at least every three cycles using standard WHO response criteria. Measurable disease was assessed by physical examination before each cycle and imaging studies every 2~3 cycles. In patients with evaluable disease, response was assessed when follow-up imaging studies, as judged by radiologists, displayed an obvious decrease in the size and/or number of lesions and by improvement in symptoms. For patients with both measurable and non-measurable sites, response was scored on the basis of the measurable disease. The National Cancer Institute of Common Toxicity Criteria version 2.0 were used to grade toxicity before each treatment cycle.
3) Statistical analysisOur primary objective was to assess the clinical outcomes and prognostic factors of gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. Our secondary objective was to compare gemcitabine monotherapy (G) with combination chemotherapy (GV/GX) with respect to response and survival. Descriptive statistics were reported as proportions and medians. Frequencies of tumor characteristics and response rates were compared using the χ2 test. Time to progression (TTP) and overall survival (OS) were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method. The log-rank test was used to compare two or more survival curves, and Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to analyze the independent predictors for survival. The time to progression (TTP) was measured from the first day of the follow-up period without disease progression, and overall survival (OS) was measured from the first day of gemcitabine-based treatment until the last day of the follow-up period or death. Survival duration was calculated from the start of chemotherapy. p values ≤0.05 were regarded as statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS 12.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL).
RESULTS1) Patient characteristicsA total of 124 patients were enrolled with a median age of 48 years (range 24~72 years). Of these patients, 58 were treated with gemcitabine alone (G), 38 with gemcitabine/vinorelbine (GV), and 28 with gemcitabine/capecitabine (GX). Patients were divided into two groups: those who received monotherapy (G) and those who received combination therapy (GV/GX). The patient and disease characteristics, as well as prior treatment histories, were generally well-matched between these two study groups. Apart from age at baseline, there were no statistically significant differences in baseline characteristics, including initial stage, hormone receptor positivity, HER2 positivity, performance state, and sites of metastasis (Table 1). Twenty patients (16.1% had received more than three prior chemotherapy regimens for metastatic disease. Prior treatments were similar between the two groups (Table 2). The median interval from initial tumor diagnosis (initial diagnosis of primary tumor or metastasis) until the first gemcitabine administration was 34.4 months (range, 3.3~143.7 months).
2) Response and survivalWe found that 109 patients were evaluable for the response, and 81 (74.3%) had at least one measurable lesion. Twenty-one patients (19.3%) exhibited a partial response and 45 patients (41.6%) had stable disease. Thus, overall disease control (objective response plus stable disease) was attained in 60.6% of patients (95% CI: 50.8~69.2%; Table 3). Time to progression (TTP) and overall survival (OS) time are shown as cumulated proportions (Fig. 1, Table 4). At a median follow-up time of 21.4 months, the median TTP was 3.1 months (95% CI; 2.0~4.2 months) and the median OS was 7.6 months (95% CI; 5.5~9.6 months).
When gemcitabine monotherapy was compared with combination therapy, the latter group demonstrated a significantly superior objective response rate, with tumor response achieved in 28.3% of patients compared with 8.2% in the single-agent group (p=0.008). Gemcitabine-based combination therapy also resulted in significantly superior TTP (log-rank p=0.028; HR 0.66; 95% CI, 0.45~0.96, Fig. 2), but OS did not differ significantly, with median survivals of 7.4 months in the monotherapy group and 8.2 months in the combination therapy group (p=0.538, HR 1.14; 95% CI, 0.75~1.73, Fig. 3).
3) Prognostic factorsUnivariate analysis showed that ECOG performance status (ECOG PS ≤2 vs. 3, p=0.000), ER/PR status (p=0.03), and the length of the disease-free interval (DFI ≤36 months vs. >36 months, p=0.03) had a significant impact on OS, whereas age (≤40 vs. >40 years), histologic grade, and the number of prior chemotherapy regimens for metastatic cancer (≤2 vs. >2) did not. In multivariate analysis using the Cox proportional hazards model, poor performance status (DFI ECOG PS ≤2 vs. 3, p<0.001, HR=2.841, 95% CI: 1.75~4.63) and a short disease-free interval (≤36 months) (p=0.005, HR=2.62, 95% CI: 1.33~5.16) predicted impaired OS. Treatment regimen was not a significant predictor of survival.
4) Toxicity and dose intensityThe median number of chemotherapy cycles received was 3 (range, 1~9; total 415). Eighty patients required dose reductions for adverse events (64.5%). The actual dose intensity was 570 mg/m2/week, ranging from 248 to 750 mg/m2/week, making the relative dose intensity 84.1%.
The frequencies of adverse events related to gemcitabine-based chemotherapy are shown in Table 5. WHO grade 3/4 toxicities were primarily hematologic, with the most common being neutropenia (40.3%) and thrombocytopenia (22.4%). Neutropenia was observed more frequently in the combination group than with gemcitabine alone (31% vs. 48.5%, p=0.048). Non-hematologic toxicities were generally infrequent. The toxicities of combination therapy were comparable to that of gemcitabine monotherapy (Table 5).
DISCUSSIONThe purpose of this study was to report our experience with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy regimens and to compare the efficacy of single agent or combination gemcitabine-based regimens. In this retrospective study, the efficacy of gemcitabine monotherapy and combination therapy for women with anthracycline- and taxane-pretreated MBC was modest. Although the combination therapy regimens were significantly superior to gemcitabine monotherapy in response rate and TTP, OS was similar in both treatment arms.
In patients with heavily pre-treated breast cancer, one of the major concerns during salvage chemotherapy is the patients' ability to tolerate treatment. Gemcitabine is therefore an appropriate choice because it has few long-term side effects, causes mild marrow suppression, and is mildly emetogenic. The efficacy of single-agent gemcitabine has been evaluated in several phase II trials. As a second-line or subsequent treatment for MBC, gemcitabine monotherapy resulted in response rates of 14~29% and median progression-free survival intervals of 4~6.3 months. These results have promoted efforts to improve the efficacy of gemcitabine by combining it with other agents such as vinorelbine, capecitabine, cisplatin and taxanes (13,14). Vinorelbine, a novel vinca alkaloid, is also an active agent in breast cancer. Recent trials with the gemcitabine/vinorelbine combination gave response rates of 22~54% with median TTPs of 3.5~8.5 months (15,16). Capecitabine, an oral fluoropyrimidine, was rationally designed to preferentially generate 5-FU in tumor tissue. In trials with this combination regimen, gemcitabine/capecitabine, the response rate was 48.7%, the median TTP was 5 months and the median OS was 10 months (17).
Compared with these results, the outcomes reported here are somewhat inferior. In the monotherapy group, we observed a response rate of 8.2% to gemcitabine and a median TTP of 2.8 months. For the gemcitabine/vinorelbine combination regimen, the response rate was 26.5% and the median TTP was 3.4 months, whereas the response rate was 30.8%, the median TTP was 4.0 months and the median OS was 10.5 months for the gemcitabine/capecitabine combination. The differences in efficacy between our study and earlier trials may be caused by variations in patient selection and previous treatments. In our study, all patients received gemcitabine for salvage therapy in metastatic setting. All had been exposed to both anthracyclines and taxanes, and 16.1% of our patients had received more than three different chemotherapy regimens for metastatic disease. In addition, some of these patients had also previously been exposed to vinorelbine or capecitabine. Our patients also had relatively poor performance status at the start of treatment. The extent of metastatic disease (65% had predominant visceral disease) may account, in part, for the short median TTP and median survival time in our study.
While combination chemotherapy is used routinely in the adjuvant setting, the use of combination treatment in the metastatic setting is more controversial. Two trials comparing taxane-anthracycline combination therapy with sequential monotherapy have not provided evidence of any advantages with the combination approach (18,19). However, newer, rationally designed combinations may offer survival advantages over single monotherapy. The combination of docetaxel and capecitabine achieved significantly superior TTP and survival with manageable toxicity profiles in anthracycline-pretreated patients (20). Likewise, in the GEICAM study, the gemcitabine and vinorelbine combination prolonged TTP compared with vinorelbine monotherapy in the salvage setting (21).
Although most phase II studies have shown that gemcitabine-based combination therapy results in better objective response rates than gemcitabine alone, both regimens yielded similar survival data. In our study, gemcitabine-based combination chemotherapy also demonstrated a higher response rate and longer time to progression. In addition, we observed no differences in significant toxicity between the combination regimens and gemcitabine alone. Likewise, treatment was generally well tolerated in all three groups, as indicated by the small number of grade 3/4 non-hematologic toxicities. For both the monotherapy and combination therapy groups, grade 3/4 toxicities were primarily hematologic, and neutropenia was the most common; neutropenia occurred more frequently in the combination group. Gemcitabine/vinorelbine treatment tended to result in more neutropenia, while gemcitabine/capecitabine was associated with capecitabine-related hand-foot syndrome. In our analysis, gemcitabine-based combination therapy is presumed to be particularly useful in patients with visceral disease and fast-growing tumors, although this was not compared with true sequential therapy.
Recently, large multi-center trials have shown that capecitabine monotherapy is a promising first- and second-line therapy for MBC (22). Moreover, this agent has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a single agent for the treatment of anthracycline- and taxane-refractory patients. Nevertheless, when we compared the efficacy of gemcitabine/vinorelbine with that of gemcitabine/capecitabine, we found no significant differences in response, TTP and OS, although gemcitabine/capecitabine showed a trend toward superior response (data not shown). Any actual differences may have been attenuated by the small sample size and the retrospective study design. Due to recent phase III results showing the superiority of gemcitabine/paclitaxel over paclitaxel alone as the first-line therapy, the combination of gemcitabine/taxanes is currently being evaluated as a second-line therapy even after prior anthracycline and/or taxanes (23,24). In addition, trials for gemcitabine with platinum or with trastuzumab in HER2 positive breast cancer patients are currently underway (13).
Our study confirmed that poor performance status and a short disease-free interval correlate with an unfavorable prognosis in patients with MBC (12). Considering that the efficacy of salvage therapy regimens is generally modest, physicians should consider a patient's prior performance, quality of life and preferences before deciding on salvage chemotherapy.
The current study had several limitations. The first was a possible selection bias between the monotherapy and combination therapy groups. However, in our institution, the choice of single or combination regimen did not depend on a patient's condition or the aggressiveness of disease, but rather was the physicians' choice. Another limitation was that patients with both measurable and non-measurable disease were included in this study; as a result, we modified the response criteria for patients with non-measurable disease by referring to previous studies (20,25). Additional drawbacks include the small sample size and the retrospective study design.
CONCLUSIONSOur results suggest that gemcitabine-based combinations are superior to gemcitabine alone in terms of tumor response and TTP prolongation as salvage therapy in MBC. However, these results still need to be demonstrated in prospective phase III trials to prove the superiority of gemcitabine combination chemotherapy over monotherapy, especially after prior treatment with anthracyclines and taxanes.
NotesThis study was supported in part by a grant from the Korean Health 21 R&D Project, Ministry of Heath & Welfare, Republic of Korea (0412-CR01-0704-0001). References1. Cardoso F, Di LA, Lohrisch C, Bernard C, Ferreira F, Piccart MJ. Second and subsequent lines of chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer: what did we learn in the last two decades? Ann Oncol. 2002;13:197–207. PMID: 11885995
2. Plunkett W, Huang P, Searcy CE, Gandhi V. Gemcitabine: preclinical pharmacology and mechanisms of action. Semin Oncol. 1996;23(5):suppl 103–15. PMID: 8893876
3. Casper ES, Green MR, Kelsen DP, Heelan RT, Brown TD, Flombaum CD, et al. Phase II trial of gemcitabine (2,2'-difluorodeoxycytidine) in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Invest New Drugs. 1994;12:29–34. PMID: 7960602
4. Cormier Y, Eisenhauer E, Muldal A, Gregg R, Ayoub J, Goss G, et al. Gemcitabine is an active new agent in previously untreated extensive small cell lung cancer (SCLC). A study of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Ann Oncol. 1994;5:283–285. PMID: 8186176
5. Anderson H, Lund B, Bach F, Thatcher N, Walling J, Hansen HH. Single-agent activity of weekly gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12:1821–1826. PMID: 8083706
6. O'Rourke TJ, Brown TD, Havlin K, Kuhn JG, Craig JB, Burris HA, et al. Phase I clinical trial of gemcitabine given as an intravenous bolus on 5 consecutive days. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A:417–418. PMID: 8204374
7. Possinger K, Kaufmann M, Coleman R, Stuart NS, Helsing M, Ohnmacht U, et al. Phase II study of gemcitabine as first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 1999;10:155–162. PMID: 10211545
8. Spielmann M, Llombart-Cussac A, Kalla S, Espie M, Namer M, Ferrero JM, et al. Single-agent gemcitabine is active in previously treated metastatic breast cancer. Oncology. 2001;60:303–307. PMID: 11408796
9. Blackstein M, Vogel CL, Ambinder R, Cowan J, Iglesias J, Melemed A. Gemcitabine as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer: a phase II trial. Oncology. 2002;62:2–8. PMID: 11810037
10. Rha SY, Moon YH, Jeung HC, Kim YT, Sohn JH, Yang WI, et al. Gemcitabine monotherapy as salvage chemotherapy in heavily pretreated metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005;90:215–221. PMID: 15830134
11. Park JY, Kim C, Sohn JH, Kim YT, Rha SY, Jang WI, et al. A phase II study of gemcitabine monotherapy in breast cancer refractory to anthracycline and taxane. Cancer Res Treat. 2002;34:274–279.
12. Dickson RB, Pestell RG, Lippman ME. In : DeVita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Cancer of the breast. Cancer: principles & practice of oncology. 2005. 7th edPhiladelphia P.A.: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; p. 1399–1487.
13. Heinemann V, Stemmler HJ, Wohlrab A, Bosse D, Losem C, Kahlert S, et al. High efficacy of gemcitabine and cisplatin in patients with predominantly anthracycline- and taxane-pretreated metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006;57:640–646. PMID: 16163537
14. Zielinski C, Beslija S, Mrsic-Krmpotic Z, Welnicka-Jaskiewicz M, Wiltschke C, Kahan Z, et al. Gemcitabine, epirubicin, and paclitaxel versus fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide as first-line chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer: a Central European Cooperative Oncology Group International, multicenter, prospective, randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1401–1408. PMID: 15735116
15. Stathopoulos GP, Rigatos SK, Pergantas N, Tsavdarides D, Athanasiadis I, Malamos NA, et al. Phase II trial of biweekly administration of vinorelbine and gemcitabine in pretreated advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:37–41. PMID: 11773151
16. Nicolaides C, Dimopoulos MA, Samantas E, Bafaloukos D, Kalofonos C, Fountzilas G, et al. Gemcitabine and vinorelbine as second-line treatment in patients with metastatic breast cancer progressing after first-line taxane-based chemotherapy: a phase II study conducted by the Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group. Ann Oncol. 2000;11:873–875. PMID: 10997817
17. Andres R, Mayordomo JI, Lara R, Lastra R, Ortega E, Polo E, et al. Gemcitabine/capecitabine in patients with metastatic breast cancer pretreated with anthracyclines and taxanes. Clin Breast Cancer. 2005;6:158–162. PMID: 16001994
18. Sledge GW, Neuberg D, Bernardo P, Ingle JN, Martino S, Rowinsky EK, et al. Phase III trial of doxorubicin, paclitaxel, and the combination of doxorubicin and paclitaxel as front-line chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer: an intergroup trial (E1193). J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:588–592. PMID: 12586793
19. Alba E, Martin M, Ramos M, Adrover E, Balil A, Jara C, et al. Spanish Breast Cancer Research GroupMulticenter randomized trial comparing sequential with concomitant administration of doxorubicin and docetaxel as first-line treatment of metastatic breast cancer: a Spanish Breast Cancer Research Group (GEICAM-9903) phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:2587–2593. PMID: 15226326
20. O'Shaughnessy J, Miles D, Vukelja S, Moiseyenko V, Ayoub JP, Cervantes G, et al. Superior survival with capecitabine plus docetaxel combination therapy in anthracycline-pretreated patients with advanced breast cancer: phase III trial results. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:2812–2823. PMID: 12065558
21. Munoz M, Martin M, Ruiz A, Balil A, Garcia-Mata J, Calvo L, et al. Phase III study of gemcitabine plus vinorelbine (VG) versus vinorelbine (V) in patients with metastatic breast cancer (MBC) previously treated with anthracyclines (A) and taxanes (T). Final results of GEICAM 2000-04 study. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2006;24:18S(abstr 575)
22. Fumoleau P, Largillier R, Clippe C, Dieras V, Orfeuvre H, Lesimple T, et al. Multicentre phase II study evaluating capecitabine monotherapy in patients with anthracycline- and taxane-pretreated metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:536–542. PMID: 14962720
23. Mavroudis D, Malamos N, Alexopoulos A, Kourousis C, Agelaki S, Sarra E, et al. Greek Breast Cancer Cooperative GroupSalvage chemotherapy in anthracycline-pretreated metastatic breast cancer patients with docetaxel and gemcitabine: a multicenter phase II trial. Ann Oncol. 1999;10:211–215. PMID: 10093691
24. Alexopoulos A, Tryfonopoulos D, Karamouzis MV, Gerasimidis G, Karydas I, Kandilis K, et al. Evidence for in vivo synergism between docetaxel and gemcitabine in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004;15:95–99. PMID: 14679126
25. Hennessy BT, Gauthier AM, Michaud LB, Hortobagyi G, Valero V. Lower dose capecitabine has a more favorable therapeutic index in metastatic breast cancer: retrospective analysis of patients treated at M. D. Anderson Cancer Center and a review of capecitabine toxicity in the literature. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:1289–1296. PMID: 15890665
Fig. 1Kaplan-Meier curves of time to progression and overall survival for all patients (n=124). TTP, time to progression; OS, overall survival. 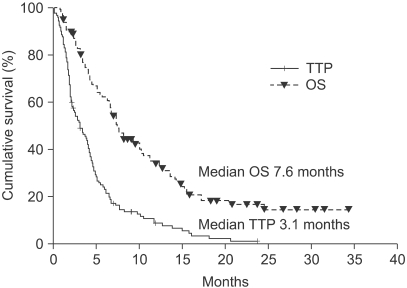
Fig. 2Kaplan-Meier curves of time to progression according to combination or monotherapy (p=0.028). G, gemcitabine; GV, gemcitabine/vinorelbine; GX, gemcitabine/capecitabine. 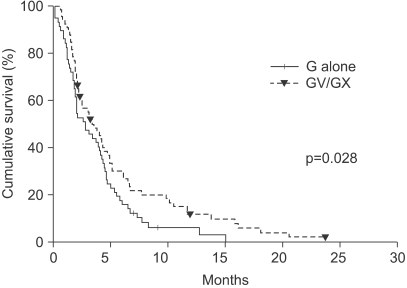
Fig. 3Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival according to combination or monotherapy (p=0.54). G, gemcitabine; GV, gemcitabine/vinorelbine; GX, gemcitabine/capecitable. 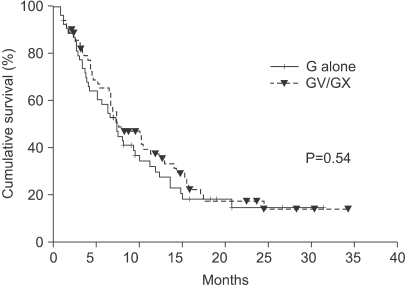
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||