AbstractCancer is a leading cause of disease-related mortality worldwide. Drug resistance is one of the primary reasons for the failure of anticancer therapy. There are a number of underlying mechanisms for anticancer drug resistance including genetic/epigenetic modifications, microenvironmental factors, and tumor heterogeneity. In the present scenario, researchers have focused on these novel mechanisms and strategies to tackle them. Recently, researchers have recognized the ability of cancer to become dormant because of anticancer drug resistance, tumor relapse, and progression. Currently, cancer dormancy is classified into “tumor mass dormancy” and “cellular dormancy.” Tumor mass dormancy represents the equilibrium between cell proliferation and cell death under the control of blood supply and immune responses. Cellular dormancy denotes the state in which cells undergo quiescence and is characterized by autophagy, stress-tolerance signaling, microenvironmental cues, and epigenetic modifications. Cancer dormancy has been regarded as the stem of primary or distal recurrent tumor formation and poor clinical outcomes in cancer patients. Despite the insufficiency of reliable models of cellular dormancy, the mechanisms underlying the regulation of cellular dormancy have been clarified in numerous studies. A better understanding of the biology of cancer dormancy is critical for the development of effective anticancer therapeutic strategies. In this review, we summarize the characteristics and regulatory mechanisms of cellular dormancy, introduce several potential strategies for targeting cellular dormancy, and discuss future perspectives.
IntroductionCancer is one of the main causes of death worldwide and a great impediment to extending life expectancy [1]. Anticancer drug resistance and tumor relapse, which may even occur several years after curative anticancer therapies, are the main causes of cancer-associated mortality [2]. Recurrent tumors are believed to emerge from a subpopulation of cells that survive anticancer treatment, and are generally referred to as minimal residual disease (MRD). They may remain in a clinically undetectable state for some years or decades and then resume growth under certain growth-favoring circumstances to develop recurrent tumors [3,4]. MRD covers the following populations: a rare subpopulation of cancer cells with resistance to anticancer therapeutics in therapy-sensitive tumors; disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) that escape from the primary tumor, survive against environmental stresses and the immune system in circulation, and arrive at and colonize distant organs in the early or late stages of cancer progression; and circulating tumor cells that move in the bloodstream or lymphatic system and finally become DTCs [4–7]. Although adjuvant therapy administered in certain cases is deemed to suppress tumor relapse by targeting the MRD, not all patients benefit from it. Therefore, MRD is considered a marker of poor prognosis in patients with cancer, and understanding the mechanisms by which tumors remain dormant or awake is fundamental for developing strategies to prevent tumor relapse. Indeed, owing to substantial progress in deciphering the mechanisms underlying cellular dormancy and awakening during the last decades, several studies have reported on the biology of cellular dormancy and potential targeting strategies [8–12]. Hence, this review article aims to provide mechanistic insights into cancer cell dormancy and awakening, discuss the implications of cellular dormancy in chemoresistance and cancer progression, and propose potential strategies to develop dormancy-targeting anticancer agents. A brief summary of the mechanisms responsible for maintenance of and escape from dormancy is presented in Fig. 1.
Tumor and Cellular DormancyTumor dormancy is a critical phase in cancer development during which tumor cells exist, but tumor progression is not clinically apparent [13]. It includes both tumor mass dormancy, referring to the presence of neoplastic masses that have achieved a balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis [8,9,14], and cellular dormancy, referring to a slow-cycling or non-proliferative state with reversible and temporal growth arrest. As described before, tumor mass dormancy is the equilibrium status between cell proliferation and cell death [8,9,15], which is further subclassified as “angiogenic dormancy” and “immunogenic dormancy” [8,9]. Angiogenic dormancy is a phenomenon that occurs prior to the angiogenic switch, in which cell proliferation and death are balanced based on the level of oxygen and nutrients supplied by the preexisting blood vessels [8,9,15]. Before the angiogenic switch, increased cell proliferation causes depletion of oxygen and nutrients in the environment distal to the blood vessel, eventually leading to cell death and an equilibrium between proliferation and the death of cancer cells [8,9,15]. Supplementation of angiogenic factors awakened dormant tumor cells and promoted tumor growth [9,16]. Immunogenic dormancy is the status of balanced cell proliferation and cell death based on surveillance of the host immune system [8,9]. Cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth can be suppressed by surveillance of the host immune system, including T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells that recognize and kill tumor cells through tumor-specific or stress-induced cell surface antigens [17]. In addition, interferon-γ (IFN-γ), produced by Th1 cells, CD8+ T cells, NK cells, and NK T cells, induces dormancy in cancer cells via signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1)–dependent or –independent pathways (for example, the indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 [IDO1]–kynurenine [Kyn]–aryl hydrocarbon receptor [AhR]–p27 pathway) [18–22]. If the host immune system cannot completely eliminate cancer cells or maintain their dormant status, the remaining cancer cells may proliferate; however, the expansion of cancer cells can be controlled by the host immune system. Therefore, an active host immune system dynamically balances the proliferation and death of cancer cells, causing immunogenic dormancy [8,9,17]. The evolution of dormant cancer cells to acquire the ability to blunt antitumor immunity causes the escape of the host immune system and the consequent outgrowth of dormant cancer cells [8,9,17]. In contrast, cellular dormancy is a state in which cells undergo quiescence, which is more consistent with the classical definition of dormancy than tumor mass dormancy [8,9]. Considering the shared features between dormant cancer cells and slow-cycling cancer cells (SCCs), such as therapy resistance, reversible cell cycle arrest, and a potential cause of tumor relapse [23,24], SCCs are also regarded as dormant or quiescent cells [23].
Identification of Dormant Cancer Cells and Their Characteristics1. Identification of dormant cancer cellsTo identify clinically relevant dormancy-associated biomarkers, it is necessary to establish experimental models of dormant cancer cells using clinical samples. Several approaches have been proposed for identifying dormant cancer cells in preclinical and clinical models. The existence of dormant cancer cells has been determined by evaluating the level of proliferation and apoptosis-related marker expression (for example, Ki67 and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling [TUNEL] expression [Ki67 and TUNEL-double-negative population is considered as the dormant population] [25]; Ki67 and M30 expression [Ki67 and M30-double negative population is considered as the dormant population] [26]), and the mitotic activity index (the total number of mitoses in 10 fields of vision according to the Multicenter Mammary Carcinoma Project protocol) [27] or mitotic index (determination of the level of phosphorylated histone H3 expression)] [28]. Several experimental approaches, such as the pulse and chase experiment using nucleotides that can be incorporated into DNA during DNA replication [for example, BrdU (5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine), EdU (5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine), or tritiated thymidine (3H-T)], label-retention methods using carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CSFE), PKH26, or DiD dyes, the labeling and chase method using a doxycycline-inducible green fluorescence protein (GFP)–tagging histone H2B (H2B-GFP) reporter, use of the Fluorescent Ubiquitination-based Cell-Cycle Indicator (FUCCI) reporter, gene promoter reporters using CDKN2A (that encodes p16) or KDM5B promoters, and a cell cycle indicator (the mVenus-p27K− probe) have been used for identification of slow-cycling/dormant cancer cells [23,29–34]. Bioencapsulation in a stiff and porous 3D matrix using synthetic materials has been recently developed for isolating dormant cancer cells [35]. Furthermore, as described in recently published literature [36,37], several in vitro models for tumor dormancy and genetically engineered mouse models for the establishment of clinically relevant in vivo dormancy models have been developed. Several methods for identifying dormant cancer cells are summarized in Table 1.
2. Main characteristics of dormant cancer cellsTypical dormancy-associated cellular changes are reversible retardation or arrest of cell proliferation, which is accompanied by cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle, induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, including p21 and p27, and downregulation of cell proliferation-related markers such as Ki67 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen [8,9,11]. Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and downregulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation (p38High/ERKLow) have been considered prototype markers of dormant cancer cells [38,39]. However, in recent studies, ERK activation was also found in cells that underwent dormancy-like states, such as cells forced to acquire dormancy-like phenotypes by incubation onto biomaterials under serum deprivation conditions [40] or those with SCC-like phenotypes (drug-tolerant persister [DTP]) by treatment with irinotecan (CPT-11) [41]. In addition, despite growth arrest and/or retardation and environmental insults, dormant cancer cells exhibit minimal cell death and harbor resistance to anticancer therapeutics [15,23,34,43]. These cells also display reduced cellular metabolism, such as decreased energy production, protein translation, and glycolysis [44,45]. Dormant cancer cells also have a compact chromatin structure due to K20 methylation of histone H4 [24,46].
3. Association of senescence with cellular dormancy in cancer cellsSeveral dormant cell characteristics, such as growth arrest and therapy resistance, appear to be shared by other cellular alterations including senescence and cancer stem cells (CSCs). Despite the potential of reversible growth arrest in senescent cells, such as escape from chemotherapy-induced senescence reported in a recent study [47], senescent cells generally undergo an irreversible growth arrest [24,48,49]. In addition, senescent cells display persistent DNA damage responses, altered chromatin structure (senescence-associated heterochromatin foci), elevated β-galactosidase (β-gal) activity, and a hypersecretory ability known as the “senescence-associated secretory phenotype” (SASP) [24,48,49]. Senescence is induced in response to various stressful stimuli such as oncogene expression and chemotherapy [48]. Despite the presence of senescence-associated characteristics in dormant cancer cells [24,48] and the similarities between senescence and dormancy (such as induction by stressful stimuli, growth arrest accompanied by p21 upregulation, and p38 MAPK activation) [24,50], several studies have shown that senescence is not always involved in the maintenance of dormant cancer cells [42,51]. In addition, the features of senescence differ from those of dormancy in terms of the reversibility of cell cycle arrest (irreversible vs. reversible), metabolic activity (high vs. low), and interaction with the immune system (immune attractive vs. immune evasive) [24]. However, regardless of similarities and differences in the regulation of intrinsic signaling changes, senescence appears to be an aspect of dormancy in tumors and contributes to the regulation of dormancy and awakening of dormant cancer cells via its SASP phenotype [24,52] and by mediating the acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and stemness phenotypes [53].
4. Association of EMT and/or CSC-like phenotypes with cellular dormancy in cancer cellsCSCs are a rare population of tumors harboring stem cell–like characteristics, such as self-renewal, symmetric or asymmetric division, differentiation capacity, therapy resistance, and tumorigenic activity [54,55]. CSCs are thought to arise from normal stem cells through the sequential acquisition of genetic or epigenetic changes, or from the dedifferentiation of progenitor cells harboring genetic mutations or non-CSCs [54,56]. CSCs are capable of generating diverse tumor cell populations and play crucial roles in tumorigenesis and cancer progression [54,57]. In addition, the EMT program is closely involved in the acquisition of stemness phenotypes [58–60]. The key cellular changes in the EMT program are the loss of polarity of epithelial cells with downregulation of epithelial markers (for example, E-cadherin) and gain of mesenchymal markers including N-cadherin, fibronectin, vimentin, Snail1, Snail2, Slug, Twist1, and zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (Zeb1), with invasive phenotypes [59]. EMT-mediated transcription factors (Snail1, Snail2, Twist1, and Zeb1) were found to induce stemness markers including sex determining region Y-box 2 (Sox2), B lymphoma Mo-MLV insertion region 1 homolog (BMI1), and octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (Oct4) [61,62]. However, the EMT activator paired related homeobox 1 (Prrx1) was found to repress stemness in cancer cells [63], indicating that both EMT and mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) programs may contribute to the acquisition of stemness phenotype [61]. Moreover, although several features of dormant cancer cells differ from those of CSCs, including the low tumor-initiating properties of dormant cancer cells compared to the high tumorigenic activity of CSCs and growth arrest (quiescence) in dormant cancer cells compared to quiescent or proliferative phenotypes in CSCs [23], studies have shown that stemness phenotypes are associated with the regulation of dormancy in cancer cells [59,64–66], implying that CSC phenotype acquisition may play a role in the modulation of dormant cancer cells. Considering the complexity of EMT regulation and stemness [61], additional studies are necessary to clarify the precise role of EMT/MET and stemness programs in the regulation of dormancy.
Mechanisms Underlying Regulation of Cancer Cell DormancyGrowth arrest in dormant cancer cells is a consequence of the intrinsic regulation of cell cycle machinery, modulation of cellular signaling through interaction with the extracellular matrix (ECM) and ECM-associated molecules, signal transduction in response to various stimuli from the surrounding microenvironment, and other cellular changes [9,11] (Fig. 2). The regulation of cellular dormancy by the aforementioned factors is detailed below.
1. Regulation of cellular dormancy by the Rb-E2F and DREAM complexesDormant cancer cells undergo cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase. Cell cycle progression is tightly and cooperatively regulated by retinoblastoma (Rb)-E2F and the dimerization partner, Rb-like, E2F, and multi-vulval class B (DREAM) complexes in a transcription-dependent manner [67], and these mediators play an important role in mediating dormancy in cancer cells. During quiescence, the Rb protein blocks cell cycle entry into the S phase by repressing the transcription of genes responsible for the cell cycle machinery via direct binding to the transactivation domain of the canonical E2F transcription factors and chromatin structure remodeling through interaction with proteins responsible for chromatin remodeling (such as human Brahma [BRM] and brahma-related gene-1 [BRG1]) and histone modification [such as histone deacetylase 1 and histone lysine methyltransferase SUV39H1] [67,68]. Cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 and cyclin E/CDK2 complexes phosphorylate Rb protein, causing the release of Rb protein with E2F and cell cycle progression [68]. In addition to Rb protein, noncanonical E2F proteins (E2F6, E2F7, and E2F8) repress the transcription of cell cycle regulators in an Rb protein-independent manner [67]. A previous study also demonstrated the association of activation threshold of the Rb-E2F network with the depth of quiescence [69].
The DREAM complex, which consists of an Rb family protein (p130/RBL2 or p107/RBL1), a repressor E2F (E2F4 or E2F5), a dimerization partner, and a multi-vulval class B (MuvB) repressor complex (Lin9, Lin37, Lin52, Lin54, and RBBP4), inhibits transcription of cell cycle regulators [67,70–72]. Phosphorylation of the Rb family protein p130 by cyclin-dependent protein kinases inhibits DREAM complex assembly, whereas inhibition of p130 phosphorylation by CDK blockade or phosphorylation of Lin52 at S28 by dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) facilitates DREAM complex assembly and promotes quiescence [71,73,74]. In addition, knockdown of the expression of Lin52 or DYRK1A [75], pharmacological inhibition of DYRK1A [76], or binding of proliferating cell nuclear antigen-associated factor to the core DREAM subunit RBBP4 [77] disrupted DREAM complex formation and caused cells to exit quiescence, indicating the important role of the DREAM complex in quiescence and cellular dormancy. Therefore, the DREAM complex could be a cellular target for regulating dormancy in cancer cells.
2. Regulation of cellular dormancy by interaction with the extracellular matrixThe ECM is a noncellular, physical, and structural component in tissues and organs that plays important roles in providing physical scaffolding and transducing cellular, biochemical, and biomechanical signaling pathways involved in the construction of cellular architectures, cellular polarity, cell proliferation, survival, motility, differentiation, and homeostasis [78–80]. More than 1,000 proteins that encode the ECM and ECM-associated proteins have been defined as “the matrisome,” and “the core matrisome,” which is composed of about 300 core ECM-associated proteins, contains repeats and/or various rearrangements of distinctive groups of domains, and constructs various types of ECM in a cell or tissue-specific manner [80,81]. Collagens, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins (such as laminins, fibronectin, and elastin) construct the core matrisome [80], and these ECM components transduce signaling via their receptors, including integrins, discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases (DDRs), syndecans, and dystroglycans [78–80].
ECM remodeling and concurrent changes in ECM-mediated signaling are believed to play an important role in the activation of dormant cancer cells, leading to recurrence and metastatic tumor formation [82]. For example, urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), which has been reported to form a stable complex with integrins [83], interacts with integrin α5β1 and facilitates fibronectin fibril deposition, thereby leading to persistent ERK activation, p38 MAPK downregulation, and a consequent increase in cancer cell proliferation [84,85]. Downregulation of uPAR or blockade of uPAR and integrin α5β1 interaction causes dormancy in cancer cells [84]. In addition, fibronectin-mediated integrin β1 signaling causes myosin light chain kinase (MLCK)-mediated myosin light chain phosphorylation, leading to cytoskeleton rearrangement, stress fiber formation, and awakening of dormant cells [86]. Fibrotic circumstances mediated by type I collagen deposition also results in exit from dormancy and outgrowth of dormant cancer cells via the activation of integrin β1 signaling [87]. We have also demonstrated the involvement of upregulated type I collagen expression and integrin signaling in the awakening of slow-cycling/dormant cancer cells [88].
Studies have shown that ECM components contribute to cellular dormancy in cancer cells. For example, cells embedded in Matrigel exhibit dormant cell phenotypes [89]. In addition, dormant cancer cells induced by incubation with biomaterials under serum deprivation conditions produce type III collagen or fibronectin and create a type III collagen– or fibronectin-enriched matrix, resulting in the maintenance of cancer cell dormancy via activation of type III collagen–DDR1–STAT1 and ανβ3/α5β1 integrin-mediated signaling pathways [40,90]. Previous studies have shown that fibronectin-mediated integrin signaling activated focal adhesion kinase (FAK)–mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)–ERK signaling is necessary for the survival of dormant cancer cells, which is in conflict with the role of ERK signaling in outgrowth but not the survival of dormant cancer cells, presumably due to the dynamics of ERK activity during the course of onset and maintenance of dormancy [40]. Moreover, an ECM glycoprotein, thrombospondin-1 [80], was elevated in dormant tumor cells [91] and promoted cellular dormancy in cancer cells by suppressing angiogenesis and activating transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) [92]. The level of thrombospondin-1 showed an inverse correlation with tumor aggressiveness and a positive correlation with favorable clinical outcomes in cancer patients [93]. Another ECM glycoprotein, osteopontin, was also found to support dormancy in leukemia cells by providing an anchor for cell adhesion [94]; however, osteopontin was found to promote invasion and aggressiveness of tumor cells and may contribute to the awakening of dormant cancer cells via its ability to bind to integrin and activate integrin-mediated signaling [93,95,96], suggesting a different role of osteopontin in cellular dormancy in a context-dependent manner.
ECM stiffness, which is determined by the density of collagen and elastin and changes in their alignment via posttranslational modification [97,98], has also shown conflicting roles in cancer dormancy, depending on experimental models. A previous study demonstrated that cancer cells cultured on stiff supports displayed a proliferative phenotype by activating integrin β1-mediated ERK, Akt, and STAT3 signaling, whereas those cultured on soft supports exhibited dormancy phenotypes with elevated stemness-related marker expression, indicating the regulation of cell proliferation and dormancy by matrix stiffness [99]. Consistently, breast cancer cell spheroids grown on stiff hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels exhibited a proliferative phenotype, whereas those grown on soft HA hydrogels displayed a dormant phenotype [100]. In contrast to the proliferative phenotype, which is sensitive to anticancer therapy in breast cancer cells exposed to stiff microenvironments using synthetic substrata, cells exposed to soft microenvironments exhibited dormant phenotypes with increased autophagy and therapy resistance [101]. However, cells grown in a stiff fibrin matrix exhibit dormant phenotypes by the induction of p21 and p27 and downregulation of integrin β3 via the Cdc42-Tet2 pathway [102]. Considering the phenotypic and metabolic heterogeneity of dormant cancer cells [40,43,103], additional single cell–based in-depth investigations are necessary to determine the precise role of cell-ECM interactions in the maintenance or outgrowth of dormant cancer cells.
3. Regulation of cellular dormancy by environmental stresses and anticancer therapyIn addition to cell cycle regulatory and ECM-associated mechanisms, extracellular stress also mediates cellular dormancy. Dormant cancer cells, including DTCs, tend to encounter stressful microenvironments such as hypoxia and nutrient deprivation [103]. Cancer cells exposed to these environmental stressors display dormant phenotypes. For instance, hypoxia mediates cancer cell dormancy by the transcriptional upregulation of EMT and stemness phenotypes [104]. In addition, CSN8, a subunit of the constitutive photomorphogenesis 9 (COP9) signalosome, positively regulates hypoxia-induced EMT and cancer cell dormancy by stabilizing hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α (HIF-1α) and promoting HIF-1α signaling pathway activation [105]. Hypoxia-inducible gene domain family member 1A (HIGD1A), a HIF-1 target gene mediating cell survival, induced dormancy by repressing cellular respiration and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production [106]. Amino acid deprivation causes autophagy as a survival mechanism in dormant ovarian cancer cells through the upregulation of aplasia Ras homolog member I (ARHI or the Ras family member 3 [DIRAS3]) an autophagy inducer [107,108]. Glucose deprivation also induced autophagy, quiescence, and chemoresistance in glioblastoma cells [109]. In addition, serum deprivation caused cellular dormancy in cancer cells by fatty acid oxidation-mediated epigenetic Nanog expression and subsequent Nanog-mediated p21 and p27 induction [110]. In addition to these environmental stresses, cancer cells subjected to androgen-deprivation therapy [111], chemotherapy [42], or concurrent blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor and MEK [112] were found to enter a dormant state. Activation of cellular stress responses, such as p53-mediated transcriptional response and integrated stress response, also mediated the spontaneous acquisition of slow-cycling phenotypes in cancer cells [113].
4. Regulation of cellular dormancy by p38 MAPKSeveral mechanisms have been suggested to regulate cellular dormancy in response to environmental stress and anticancer therapies. Various environmental and cellular stresses cause cellular dormancy and activate several adaptive programs to endure cellular insults and maintain survival. Among the various signaling mediators, activation of p38 MAPK plays an important role in the induction of cellular dormancy and survival of dormant cancer cells [38,114]. p38 MAPK blocks cell cycle progression and induces quiescence by downregulating cyclins and upregulating CDK inhibitors (such as p21, p27, and p16) through the upregulation of nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group F member 1 (NR2F1), basic helix-loop-helix domain containing, class B, 3 (BHLHB3), and p53, and downregulation of c-Jun and forkhead box protein M1 (FoxM1) [38,115,116]. In addition, p38 MAPK exerts both proapoptotic effects by phosphorylation of the Bcl-2 family protein, Bim (EL), and activation of caspase-3, and prosurvival effects through increase in cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and antiapoptotic inflammatory mediators [114,117–119]. Moreover, as a prosurvival mechanism of dormant cancer cells, p38 MAPK induces the nuclear translocation and activation of activating transcription factor 6 alpha (ATF6α), leading to the induction of Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb) and 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78)/BiP/HSPA5 and, in turn, causes activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling and protection from Bax-mediated apoptosis [38,120–122]. Additionally, mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1 (MSK1), a downstream target of p38 MAPK, controls markers of stemness and differentiation [123]. Thus, activation of p38 MAPK is essential for maintenance of cellular dormancy in various aspects.
5. Regulation of cellular dormancy by autophagy inductionInduction of autophagy, a self-clearance process that maintains cellular homeostasis by lysosomal degradation of malfunctioning organelles and unfolded or aggregated proteins [124,125], also plays an important role in the survival of dormant cancer cells. Among the three types of autophagy, including macroautophagy (generally known as autophagy), microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy [124, 125], only macroautophagy (autophagy) is known to contribute to cellular dormancy [125–127]. For example, autophagy plays a crucial role in the survival of gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells that undergo quiescence following treatment with imatinib mesylate [128] and the survival of disseminated breast cancer cells that enter a dormant state [129]. In addition, the tumor suppressor gene ARHI (also known as DIRAS3) was found to be critical for the survival of dormant ovarian cancer cells grown under in vivo conditions by inducing autophagy through inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mTOR signaling, elevation of autophagy-related gene 4 (ATG4), along with the cleavage of light chain 3 (LC3) in autophagosomes [130]. DIRAS3/ARHI also maintains the survival of dormant ovarian cancer cells after treatment with conventional chemotherapeutic agents by facilitating the formation of the autophagosome initiation complex by binding to beclin 1 (BECN1) and inducing autophagy [131]. Moreover, autophagy has been found to be involved in the maintenance of diapause-like states in DTPs [41]. Despite the weak association of autophagy with slow-cycling/dormant cancer cells in our recent finding [42], these findings imply the essential role of autophagy in the control of cellular dormancy.
6. Regulation of cellular dormancy by growth factorsSeveral growth factors, derived autonomously or from stromal cells in the surrounding microenvironment, are also involved in the induction and maintenance of cancer cell dormancy. The TGF-β superfamily consists of more than 30 members of growth factors that play a pivotal role in cell proliferation, growth, survival, and differentiation, playing both tumor-suppressive and tumor-promoting roles in cancer [132]. Recent studies have demonstrated the role of TGF-β2 and bone morphogenic protein-7 (BMP-7) in cancer cell dormancy. TGF-β2 derived from the microenvironment in bone marrow (BM) caused dormancy of DTCs through TGFβR3-mediated p38 MAPK activation, p27 induction, and CDK4 downregulation [133]. Growth arrest specific 6 (Gas6)/Axl signaling and the consequent induction of TGF-β2/TGFβR also induced dormancy in disseminated prostate cancer cells [134]. In addition, BMP-7 derived from stromal cells in the BM microenvironment caused dormancy of prostate cancer cells through the activation of BMP-7/BMPR2–mediated upregulation of p38 MAPK and N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 (NDRG1) [135]. Moreover, insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), which are known to play an important role in the growth, proliferation, survival, differentiation, and metastasis of cancer cells [136], have been found to be associated with cancer cell dormancy. After ablation of oncogenic drivers, dormant residual pancreatic cancer cells (mutant Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog [KRAS] [KRASG12D/+] and c-MYC) maintain their survival by the autocrine activation of IGF1/IGF-1R and downstream Akt signaling as a compensatory mechanism [137]. IGF2 also caused dormancy and chemoresistance in osteosarcoma cells by downregulating the conventional IGF-1R/Akt signaling and enhancing autophagy and glutamine utilization [138]. Given the impact of IGFs on the promotion of cancer cell proliferation [136] and the context-dependent modulation of cell proliferation by IGF1 [139], additional studies are necessary to elucidate how IGFs determine cell fate (dormancy or proliferation) under certain circumstances.
7. Epigenetic mechanismsDormant cancer cells are able to intersperse dormancy and proliferation through epigenetic reprogramming mechanisms, including DNA methylation and histone modifications [54,55]. The expression of orphan nuclear receptor NR2F1 is suppressed in various cancers through promoter hypermethylation but becomes highly expressed during dormancy [56]. NR2F1 induces global chromatin repression by activating NANOG, leading to dormancy of DTCs in the BM [116]. Additionally, transcription factor SOX9, retinoic acid receptor β, and CDK inhibitors are known to mediate NR2F1-induced quiescence [116]. Concerning deregulation of microRNAs, a known epigenetic modulator [140], a consensus signature of human tumor dormancy-associated miRNAs (DmiRs) has been identified in human dormant breast carcinoma, glioblastoma, osteosarcoma, and liposarcoma tumors [141]. Moreover, a stable microRNA (miRNA, miR) switch has been shown to regulate dormant to proliferating phenotype transition [141]. For example, it has been shown that upregulation of miR-101 concurrently activates a number of molecules associated with dormant CSC phenotype, such as enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2)- and TP53- related proteins [142]. In addition, overexpression of miR-90 causes the formation of dormant microtumors in glioblastoma and osteosarcoma cells and inhibits tumor progression by modulating transcription factors, tumor suppressor genes, and interferon response pathways [143]. Hence, microRNAs as well as DNA or histone modifications are also implicated in the regulation of cellular dormancy.
8. Regulation of cellular dormancy by control of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated unfolded protein responseEnvironmental stresses, including hypoxia and glucose deprivation, and deregulated ECM-mediated signaling are known to disrupt homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) [45,144], resulting in the induction of ER stress and subsequent activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR), which determines cell fate depending on the duration and/or magnitude of stress [145]. Among the three branches of UPR, protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), ATF6α, and inositol requiring enzyme 1 alpha (IRE1α), ATF6α and IRE1α branches mediate the clearance of misfolded proteins from the ER by inducing transcription of genes regulating protein folding or degradation (ER-associated protein degradation, ERAD) in the ER, whereas the PERK branch causes global attenuation of protein translation by phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2α) to reduce the load of misfolded proteins and facilitate the repair of ER homeostasis [146,147]. The processing (cleavage) of ATF6 by site-1 and site-2 proteases (S1P and S2P) in the Golgi apparatus and the splicing of X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) through IRE1α are required for transcriptional activity and full activation of the UPR [148]; IRE1α also mediates regulated IRE1-dependent decay of mRNA (RIDD), resulting in both survival and death of the cells by preserving ER homeostasis and causing the decay of pre-microRNAs, respectively [149]. In addition, the PERK-eIF2α pathway eventually induces ATF4, thereby regulating cell survival and death via growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein (GADD) 34-mediated eIF2α dephosphorylation and GADD153/CHOP-mediated apoptosis [146,147]. However, protein overload through ATF4 overexpression also caused ROS production and apoptotic cell death [150]. Dormant cancer cells regulate UPR for survival. For example, the UPR is activated in DTCs and mediates their survival against hypoxic and glucose deprivation [151]. In addition, disseminated pancreatic cancer cells exhibit elevated PERK pathway activation with diminished activation of the IRE1α pathway, resulting in the acquisition of a quiescent phenotype and escape from CD8+ T cell–mediated antitumor immunity via lack of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHCI) expression [152]. Activation of p38 MAPK protects dormant cancer cells from chemotherapy-induced ER stress by increasing GRP78/BiP expression and PERK activation [153].
9. Regulation of cellular dormancy by control of ER stress–mediated protein translationTranslational control during ER stress is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and promoting cell survival [154], and, as described above, dormant cancer cells utilize UPR for survival. However, the underlying mechanisms remain to be determined. We have found altered regulation of the UPR in slow-cycling/dormant cancer cells that were identified according to CSFE dye retention or enriched by chronic treatment with chemotherapeutic agents [42]. These SCC cells exhibited typical dormancy-like phenotypes, such as an elevated p38 MAPK/ERK ratio (p38High/ERKLow), decreased expression of cyclins and CDKs, and increased expression of CDK inhibitors (p21 and p27) without senescence, stemness, and EMT-like phenotypes [42]. In addition, these SCC cells displayed upregulation of ATF6 and IRE1 target genes (such as chaperones and ERAD-associated genes) and downregulation of ATF4 protein and its target genes, such as GADD34 and CHOP, with elevated PERK and eIF2α phosphorylation [42]. Mechanistically, the regulator of G protein signaling 2 (RGS2), a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) [155], was elevated in these SCCs, causing ubiquitin-mediated degradation of ATF4 by direct binding and sustained translational arrest [42]. These findings imply that the regulation of UPR machinery for ER homeostasis is involved in the survival of dormant cancer cells upon sustained ER stress, such as chemotherapy. In addition, along with the GAP-independent role of RGS2, which includes translational control [156] and a component of cellular stress response [157–159], these findings suggest a novel function of RGS2 in the survival of dormant cancer cells by maintaining protein homeostasis against sustained ER stress caused by chemotherapy or hostile microenvironments (Fig. 3).
Awakening of Dormant Cancer CellsAs discussed in previously published literature in more detail, the breakdown of the aforementioned maintenance mechanisms of cellular dormancy under the coordinated influence of several factors, including ECM composition, direct or soluble factor-mediated indirect interaction with surrounding stromal cells in the microenvironment, nutritional availability, chronic inflammation, and other host factors, mediates the awakening of dormant cells and the formation of recurrent tumors [13,24,43,160]. In addition to the autonomous changes of autocrine soluble factors [161], the interaction with stromal cells, such as myeloid cells (macrophages, myeloid-derived suppressor cells [MDSCs], and neutrophils), pericytes, fibroblasts, and vascular endothelial cells via growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines, plays a crucial role in recurrent tumor formation [13,24,160]. For example, tissue-resident macrophages in the mammary gland are a major source of tumor-associated macrophages and mediate local recurrence and distal metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer [162]. The increase in C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) and induced mobilization of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) receptor-expressing monocytic MDSC through the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14) has also been suggested as a mechanism of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation [163]. In addition, sustained inflammation caused by bacterial infection or tobacco smoking induces the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps and extracellular DNA scaffolds bound to ECM, such as laminin, and contains cytotoxic proteins and proteases (such as neutrophil elastase and matrix metalloproteinase 9), consequently evoking the proliferation of dormant cancer cells in the lungs by the activation of integrin-mediated FAK/ERK/MLCK/Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP) signaling through a series of sequential protease-mediated laminin remodeling [164]. Activated hepatic stellate cells, the liver-specific pericytes, were found to awaken dormant breast cancer cells in the liver by releasing CXCL12 and causing CXCR4-mediated quiescence in NK cells and CXCR4-induced outgrowth of dormant cancer cells [19]. Moreover, fibroblast proliferation and microvessel formation were found to exist prior to recurrent tumor formation after radiation [165], and several studies including ours demonstrated the outgrowth of SCCs/dormant cancer cells by increasing the recruitment of fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells under cytokine- and growth factor–mediated proinflammatory and proliferation-promoting circumstances [88,166,167] (Fig. 4). In summary, the interaction with the surrounding microenvironment can be a cue for awakening dormant cancer cells and outgrowth of recurrent tumors, and strategies targeting these interactions can prevent recurrent tumor formation.
Targeting Dormant Cancer CellsThe development of therapeutic approaches targeting dormant cancer cells is significant. Based on recent findings on the regulatory mechanisms of cellular dormancy and reactivation, several strategies for targeting cancer cell dormancy and blocking recurrent tumor formation have been suggested [11–13,24]. In a recent paper, Recasens and Munoz suggested three potential strategies, termed as “Sleeping strategy,” “Awakening strategy,” and “Killing strategy” to maintain, awaken, or eradicate of dormant cancer cells [12]. The sleeping strategy prevents dormant cancer cells from entering the proliferative status [12] by suppressing integrin-mediated proliferative signaling pathways (for example uPAR, β1 integrin, MLCK, Src, and ERK) [84,86,87], epigenetically inducing dormancy-associated factors (such as induction of NR2F1 by treatment with 5-Aza-C, a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor, either alone or in combination with all-trans-retinoic acid) [116], and treating dormancy-inducing soluble factors, such as TGF-β2 and BMP-7 [133,135]. The awakening strategy makes dormant cells vulnerable to anticancer therapy that targets proliferative cells by forcing them to enter the cell cycle [12]. In our previous study, genomic ablation or RGS2 expression or an increase in protein translation by treatment with a clinically available phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitor (sildenafil, for example) induced the proliferation of SCC/dormant cells but enhanced the antitumor efficacy when combined with chemotherapeutic agents [42]. Despite the possibility of aggressive recurrent tumor formation at the primary and distal sites [12], this strategy may be effective in combination with appropriate anticancer therapeutics. Finally, the killing strategy eliminates dormant cancer cells [12]. For example, treatment with IFN-γ combined with an inhibitor of IDO1 or AhR inhibits dormant cancer cells [102]. In addition, in a pancreatic cancer model, inhibition of IGF-1R reduced MRD [137]. Targeting Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 (ULK1) combined with CPT-11 can also diminish the regrowth of dormant cancer cells [41]. In the case of dormant cancer cells with senescence-like phenotypes, using senolytic drugs that target senescent cells could be a strategy to kill dormant cancer cells [24]. In our previous study, treatment with chemotherapy in combination with clinically available Src or COX-2 inhibitors inhibited the growth of SCC/dormant cancer cells [88]. Examples of targeting dormant cancer cells are listed in Table 2. Because potential targeting strategies for dormant cancer cells have both advantages and disadvantages [12], a combinatorial approach utilizing one of these strategies would be appropriate to achieve complete elimination of dormant cancer cells. In addition, the development of new drugs that modulate a new dormancy-associated cellular target, or those with better efficacy and reduced toxicity, will be promising. Moreover, repurposing existing clinically available drugs, as demonstrated in our recent publications [42,88], would be beneficial for developing clinically relevant therapeutic strategies.
Conclusions and PerspectiveTumor dormancy is a critical step in cancer development and drug resistance [11,13,24,160]. Mechanistic insights into cellular and tumor dormancy are essential to understand how tumor cells become dormant or awaken, to prevent tumor relapse and progression, and to maximize therapeutic benefits. Despite its importance, understanding the biology of tumor dormancy has been limited because of the lack of appropriate methodologies to model dormancy in experimental models or to detect dormant cancer cells in clinical samples. However, in recent decades, several experimental approaches to mimic dormancy have been developed, including the use of genetically engineered mouse models [37] and technologies to detect dormant cancer cells using tissue or liquid biopsies [168,169]. Given the heterogeneity of dormant cancer cells and their cellular dynamics [40], such as cellular and phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity in EMT [170,171], it is likely that a plethora of intracellular and extracellular factors rewire proliferative and metabolic status in dormant cancer cells through highly dynamic processes in cooperation with various components in the microenvironment at primary and metastatic sites. Therefore, the answers are likely to be complicated. Further studies are required to identify dormancy-associated cellular markers using in-depth investigation of dormant cancer cells at the single-cell level. Such advances will aid in a better understanding of the mechanisms involved in the course of entry and exit from cellular dormancy and prevent the development of recurrent tumor formation through the diagnosis of dormant cancer cells at an early stage. These endeavors would help protect cancer survivors from fatal clinical outcomes and lower the health and socioeconomic burden of cancer.
AcknowledgmentsThis work was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), Republic of Korea (No. NRF-2016R1A3B1908631).
Fig. 1Mechanisms underlying maintenance and awakening of dormant cancer cells. Cancer dormancy is classified as tumor mass dormancy and cellular dormancy. Tumor mass dormancy is the equilibrium between cell proliferation and cell death, which is regulated by blood supply and the immune system. Cellular dormancy is the status of reversible growth arrest and characterized by cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle, induction of CDK inhibitors, reduction of proliferation markers (such as Ki67 and PCNA), p38 MAPK activation, compacted chromatin structure, and reduction of cellular metabolism. Several mechanisms, such as autophagy, stress-tolerance signaling, microenvironmental cues, and epigenetic modifications, are involved in the maintenance of cellular dormancy. Dormant cancer cells escape from the dormant status via changing autocrine soluble factors autonomously and/or interacting with surrounding stromal cells in the microenvironments. CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen. 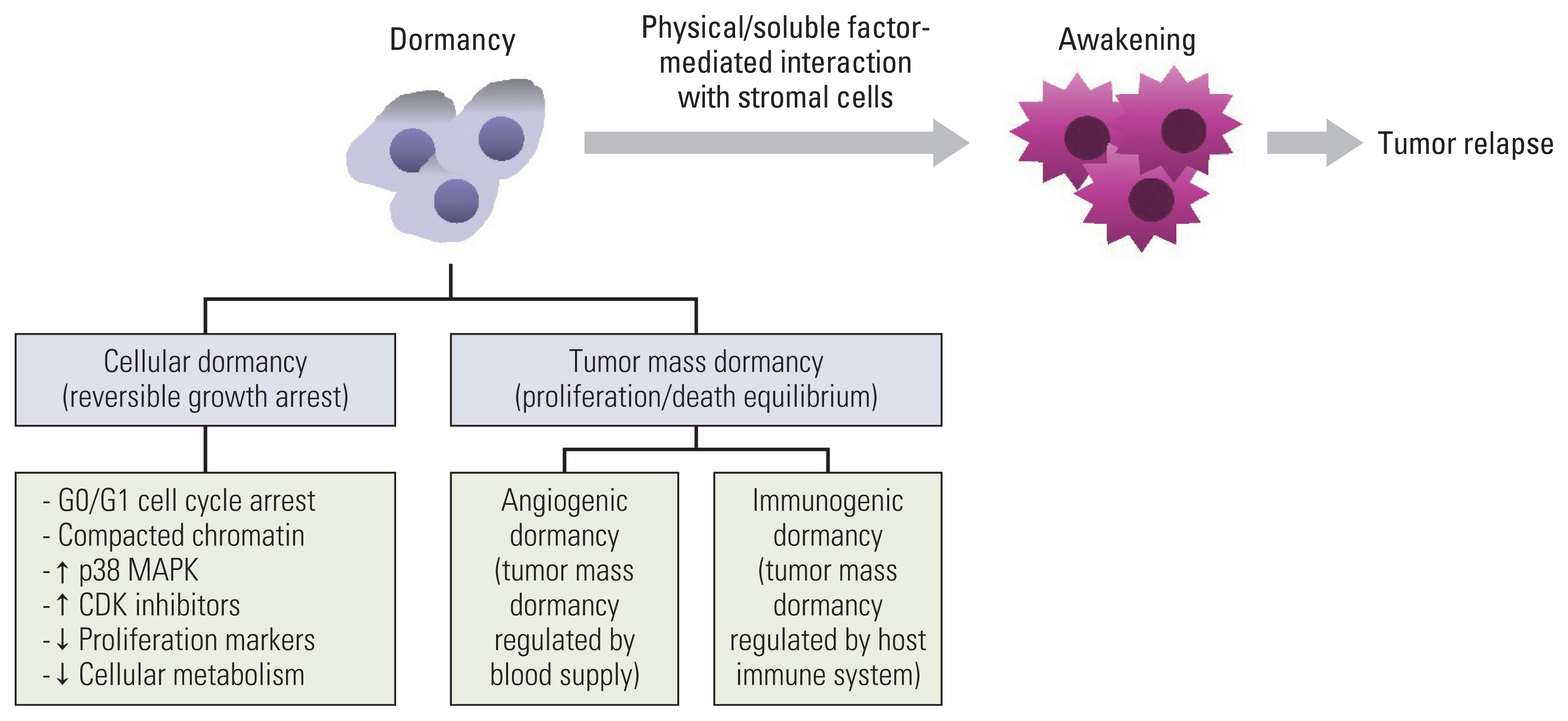
Fig. 2Intracellular modulation involved in cellular dormancy. Regulation of cell cycle machinery, such as the Rb-E2F and DREAM complexes, ECM-mediated signal transduction, p38 MAPK activation, growth factors (TGF-β family growth factors and IGFs), and ER stress-induced UPR and acquisition of senescence, autophagy, EMT, and cancer stem cell–associated phenotypes are known to be associated with cellular dormancy. DREAM, dimerization partner, Rb-like, E2F and multi-vulval class B; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; Rb, retinoblastoma; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; UPR, unfolded protein response. 
Fig. 3A proposed mechanism underlying the regulation of dormant cancer cells. Regulation of the UPR machinery for ER homeostasis is essential for the survival of dormant cancer cells in the presence of sustained ER stress, such as chemotherapy. RGS2 plays an important role in the survival of dormant cancer cells by maintaining protein homeostasis against chemotherapy or hostile microenvironments. ATF, activating transcription factor; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ERAD, ER-associated protein degradation; IRE1, inositol requiring enzyme 1; PERK, protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; RGS2, regulator of G protein signaling 2; Ub, ubiquitin; UPR, unfolded protein response; XBP1, X-box binding protein 1. 
Fig. 4Tumor relapse by awakening slow-cycling/dormant cancer cells through interaction with stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment. Increased recruitment of fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells under proinflammatory and proliferation-promoting conditions mediated by various cytokines and growth factors stimulate the proliferation of slow-cycling/dormant cancer cells, leading to relapsed tumor formation and cancer progression. ACC, active-cycling cancer cells; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; IL, interleukin; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; SCC, slow-cycling cancer cells; TGF-β2, transforming growth factor-β2. 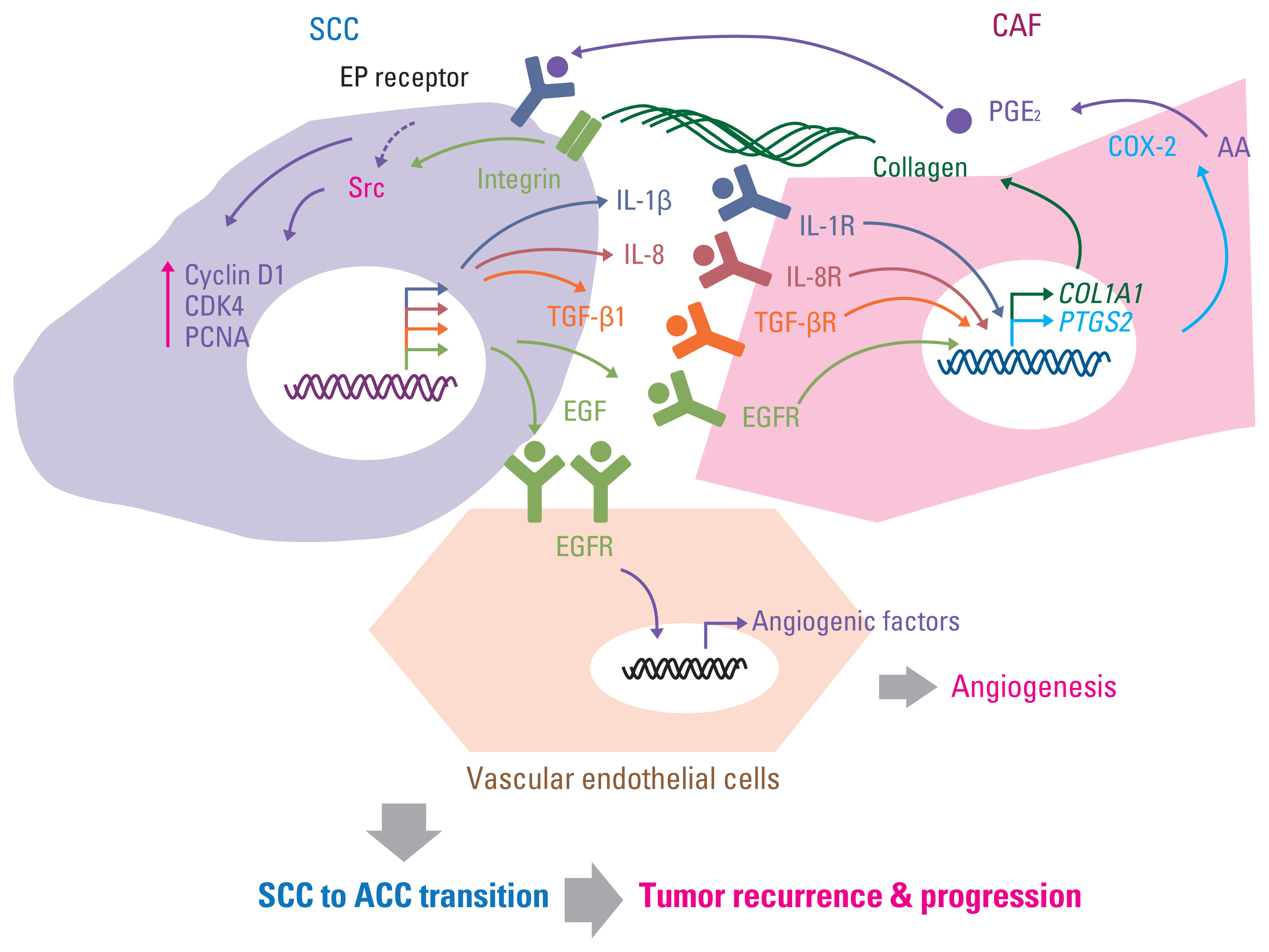
Table 1Methods for identifying dormant cancer cells
Table 2Examples of targeting dormant cancer cells
AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; BMP-7, bone morphogenic protein-7; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; IDO1, indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; NR2F1, nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group F member 1; PDE5, phosphodiesterase 5; RGS2, regulator of G protein signaling 2; TGF-β2, transforming growth factor-β2; ULK1, Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1. References1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
2. Wang X, Zhang H, Chen X. Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019;2:141–60.
3. Ruth JR, Pant DK, Pan TC, Seidel HE, Baksh SC, Keister BA, et al. Cellular dormancy in minimal residual disease following targeted therapy. Breast Cancer Res. 2021;23:63.
4. Tachtsidis A, McInnes LM, Jacobsen N, Thompson EW, Saunders CM. Minimal residual disease in breast cancer: an overview of circulating and disseminated tumour cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016;33:521–50.
5. Kang Y, Pantel K. Tumor cell dissemination: emerging biological insights from animal models and cancer patients. Cancer Cell. 2013;23:573–81.
6. Badia-Ramentol J, Linares J, Gomez-Llonin A, Calon A. Minimal residual disease, metastasis and immunity. Biomolecules. 2021;11:130.
7. Mohme M, Riethdorf S, Pantel K. Circulating and disseminated tumour cells: mechanisms of immune surveillance and escape. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14:155–67.
8. Yeh AC, Ramaswamy S. Mechanisms of cancer cell dormancy: another hallmark of cancer? Cancer Res. 2015;75:5014–22.
10. Goss PE, Chambers AF. Does tumour dormancy offer a therapeutic target? Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:871–7.
11. Damen MP, van Rheenen J, Scheele C. Targeting dormant tumor cells to prevent cancer recurrence. FEBS J. 2021;288:6286–303.
13. Sosa MS, Bragado P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA. Mechanisms of disseminated cancer cell dormancy: an awakening field. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:611–22.
15. Aguirre-Ghiso JA. Models, mechanisms and clinical evidence for cancer dormancy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:834–46.
16. Indraccolo S, Stievano L, Minuzzo S, Tosello V, Esposito G, Piovan E, et al. Interruption of tumor dormancy by a transient angiogenic burst within the tumor microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:4216–21.
18. Aqbi HF, Wallace M, Sappal S, Payne KK, Manjili MH. IFN-gamma orchestrates tumor elimination, tumor dormancy, tumor escape, and progression. J Leukoc Biol. 2018;103:1219–23.
19. Correia AL, Guimaraes JC, Auf der Maur P, De Silva D, Trefny MP, Okamoto R, et al. Hepatic stellate cells suppress NK cell-sustained breast cancer dormancy. Nature. 2021;594:566–71.
20. Liu Y, Liang X, Yin X, Lv J, Tang K, Ma J, et al. Blockade of IDO-kynurenine-AhR metabolic circuitry abrogates IFN-gamma-induced immunologic dormancy of tumor-repopulating cells. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15207.
21. Muller-Hermelink N, Braumuller H, Pichler B, Wieder T, Mailhammer R, Schaak K, et al. TNFR1 signaling and IFN-gamma signaling determine whether T cells induce tumor dormancy or promote multistage carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:507–18.
22. Braumuller H, Wieder T, Brenner E, Assmann S, Hahn M, Alkhaled M, et al. T-helper-1-cell cytokines drive cancer into senescence. Nature. 2013;494:361–5.
23. Basu S, Dong Y, Kumar R, Jeter C, Tang DG. Slow-cycling (dormant) cancer cells in therapy resistance, cancer relapse and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;78:90–103.
26. Spiliotaki M, Mavroudis D, Kapranou K, Markomanolaki H, Kallergi G, Koinis F, et al. Evaluation of proliferation and apoptosis markers in circulating tumor cells of women with early breast cancer who are candidates for tumor dormancy. Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16:485.
27. Gilje B, Nordgard O, Tjensvoll K, Janssen EA, Soiland H, Smaaland R, et al. Mitotic activity and bone marrow micrometastases have independent prognostic value in node positive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;128:137–46.
29. Oki T, Nishimura K, Kitaura J, Togami K, Maehara A, Izawa K, et al. A novel cell-cycle-indicator, mVenus-p27K-, identifies quiescent cells and visualizes G0–G1 transition. Sci Rep. 2014;4:4012.
30. Moore N, Houghton J, Lyle S. Slow-cycling therapy-resistant cancer cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21:1822–30.
31. Yumoto K, Berry JE, Taichman RS, Shiozawa Y. A novel method for monitoring tumor proliferation in vivo using fluorescent dye DiD. Cytometry A. 2014;85:548–55.
32. Chauvistre H, Shannan B, Daignault-Mill SM, Ju RJ, Picard D, Egetemaier S, et al. Persister state-directed transitioning and vulnerability in melanoma. Nat Commun. 2022;13:3055.
33. Tario JD Jr, Humphrey K, Bantly AD, Muirhead KA, Moore JS, Wallace PK. Optimized staining and proliferation modeling methods for cell division monitoring using cell tracking dyes. J Vis Exp. 2012;e4287.
34. Ebinger S, Ozdemir EZ, Ziegenhain C, Tiedt S, Castro Alves C, Grunert M, et al. Characterization of rare, dormant, and therapy-resistant cells in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:849–62.
35. Preciado JA, Aksan A. Method to isolate dormant cancer cells from heterogeneous populations. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2394:19–29.
36. Pradhan S, Sperduto JL, Farino CJ, Slater JH. Engineered in vitro models of tumor dormancy and reactivation. J Biol Eng. 2018;12:37.
37. Gu Y, Bui T, Muller WJ. Exploiting mouse models to recapitulate clinical tumor dormancy and recurrence in breast cancer. Endocrinology. 2022;163:bqac055.
38. Sosa MS, Avivar-Valderas A, Bragado P, Wen HC, Aguirre-Ghiso JA. ERK1/2 and p38alpha/beta signaling in tumor cell quiescence: opportunities to control dormant residual disease. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:5850–7.
39. Aguirre-Ghiso JA, Estrada Y, Liu D, Ossowski L. ERK(MAPK) activity as a determinant of tumor growth and dormancy; regulation by p38(SAPK). Cancer Res. 2003;63:1684–95.
40. Barney LE, Hall CL, Schwartz AD, Parks AN, Sparages C, Galarza S, et al. Tumor cell-organized fibronectin maintenance of a dormant breast cancer population. Sci Adv. 2020;6:eaaz4157.
41. Rehman SK, Haynes J, Collignon E, Brown KR, Wang Y, Nixon AM, et al. Colorectal cancer cells enter a diapause-like DTP state to survive chemotherapy. Cell. 2021;184:226–42.
42. Cho J, Min HY, Lee HJ, Hyun SY, Sim JY, Noh M, et al. RGS2-mediated translational control mediates cancer cell dormancy and tumor relapse. J Clin Invest. 2021;131:e136779.
43. Pranzini E, Raugei G, Taddei ML. Metabolic features of tumor dormancy: possible therapeutic strategies. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14:547.
44. Valcourt JR, Lemons JM, Haley EM, Kojima M, Demuren OO, Coller HA. Staying alive: metabolic adaptations to quiescence. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:1680–96.
45. Ranganathan AC, Adam AP, Zhang L, Aguirre-Ghiso JA. Tumor cell dormancy induced by p38SAPK and ER-stress signaling: an adaptive advantage for metastatic cells? Cancer Biol Ther. 2006;5:729–35.
46. Evertts AG, Manning AL, Wang X, Dyson NJ, Garcia BA, Coller HA. H4K20 methylation regulates quiescence and chromatin compaction. Mol Biol Cell. 2013;24:3025–37.
47. Milanovic M, Fan DN, Belenki D, Dabritz JH, Zhao Z, Yu Y, et al. Senescence-associated reprogramming promotes cancer stemness. Nature. 2018;553:96–100.
48. Truskowski K, Amend SR, Pienta KJ. Dormant cancer cells: programmed quiescence, senescence, or both? Cancer Meta-stasis Rev. 2023;42:37–47.
49. Schmitt CA, Wang B, Demaria M. Senescence and cancer: role and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19:619–36.
50. Iwasa H, Han J, Ishikawa F. Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 defines the common senescence-signalling pathway. Genes Cells. 2003;8:131–44.
51. Prunier C, Alay A, van Dijk M, Ammerlaan KL, van Gelderen S, Marvin DL, et al. Breast cancer dormancy is associated with a 4NG1 state and not senescence. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2021;7:140.
52. Triana-Martinez F, Loza MI, Dominguez E. Beyond tumor suppression: senescence in cancer stemness and tumor dormancy. Cells. 2020;9:346.
53. Saleh T, Tyutyunyk-Massey L, Gewirtz DA. Tumor cell escape from therapy-induced senescence as a model of disease recurrence after dormancy. Cancer Res. 2019;79:1044–6.
54. Plaks V, Kong N, Werb Z. The cancer stem cell niche: how essential is the niche in regulating stemness of tumor cells? Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16:225–38.
55. Desai A, Yan Y, Gerson SL. Concise reviews: cancer stem cell targeted therapies: toward clinical success. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8:75–81.
56. Pattabiraman DR, Weinberg RA. Tackling the cancer stem cells: what challenges do they pose? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13:497–512.
58. Lambert AW, Weinberg RA. Linking EMT programmes to normal and neoplastic epithelial stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:325–38.
59. Weidenfeld K, Barkan D. EMT and stemness in tumor dormancy and outgrowth: are they intertwined processes? Front Oncol. 2018;8:381.
60. Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell. 2008;133:704–15.
61. Pradella D, Naro C, Sette C, Ghigna C. EMT and stemness: flexible processes tuned by alternative splicing in development and cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:8.
62. Wang SS, Jiang J, Liang XH, Tang YL. Links between cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Onco Targets Ther. 2015;8:2973–80.
63. Ocana OH, Corcoles R, Fabra A, Moreno-Bueno G, Acloque H, Vega S, et al. Metastatic colonization requires the repression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition inducer Prrx1. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:709–24.
64. Jia Q, Yang F, Huang W, Zhang Y, Bao B, Li K, et al. Low Levels of Sox2 are required for melanoma tumor-repopulating cell dormancy. Theranostics. 2019;9:424–35.
65. Ohta Y, Fujii M, Takahashi S, Takano A, Nanki K, Matano M, et al. Cell-matrix interface regulates dormancy in human colon cancer stem cells. Nature. 2022;608:784–94.
66. Zhou N, Wu X, Yang B, Yang X, Zhang D, Qing G. Stem cell characteristics of dormant cells and cisplatin-induced effects on the stemness of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10:2495–504.
67. Fischer M, Schade AE, Branigan TB, Muller GA, DeCaprio JA. Coordinating gene expression during the cell cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022;47:1009–22.
69. Kwon JS, Everetts NJ, Wang X, Wang W, Della Croce K, Xing J, et al. Controlling depth of cellular quiescence by an Rb-E2F network switch. Cell Rep. 2017;20:3223–35.
70. Sadasivam S, DeCaprio JA. The DREAM complex: master coordinator of cell cycle-dependent gene expression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:585–95.
71. Litovchick L, Florens LA, Swanson SK, Washburn MP, DeCaprio JA. DYRK1A protein kinase promotes quiescence and senescence through DREAM complex assembly. Genes Dev. 2011;25:801–13.
72. MacDonald J, Ramos-Valdes Y, Perampalam P, Litovchick L, DiMattia GE, Dick FA. A systematic analysis of negative growth control implicates the DREAM complex in cancer cell dormancy. Mol Cancer Res. 2017;15:371–81.
73. Guiley KZ, Liban TJ, Felthousen JG, Ramanan P, Litovchick L, Rubin SM. Structural mechanisms of DREAM complex assembly and regulation. Genes Dev. 2015;29:961–74.
74. Schade AE, Oser MG, Nicholson HE, DeCaprio JA. Cyclin D-CDK4 relieves cooperative repression of proliferation and cell cycle gene expression by DREAM and RB. Oncogene. 2019;38:4962–76.
75. Boichuk S, Parry JA, Makielski KR, Litovchick L, Baron JL, Zewe JP, et al. The DREAM complex mediates GIST cell quiescence and is a novel therapeutic target to enhance imatinib-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2013;73:5120–9.
76. Wang P, Karakose E, Argmann C, Wang H, Balev M, Brody RI, et al. Disrupting the DREAM complex enables proliferation of adult human pancreatic beta cells. J Clin Invest. 2022;132:e157086.
77. Kim MJ, Cervantes C, Jung YS, Zhang X, Zhang J, Lee SH, et al. PAF remodels the DREAM complex to bypass cell quiescence and promote lung tumorigenesis. Mol Cell. 2021;81:1698–714.
78. Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:4195–200.
80. Hynes RO, Naba A. Overview of the matrisome: an inventory of extracellular matrix constituents and functions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4:a004903.
81. Naba A, Clauser KR, Ding H, Whittaker CA, Carr SA, Hynes RO. The extracellular matrix: Tools and insights for the “omics” era. Matrix Biol. 2016;49:10–24.
82. Winkler J, Abisoye-Ogunniyan A, Metcalf KJ, Werb Z. Concepts of extracellular matrix remodelling in tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5120.
83. Wei Y, Lukashev M, Simon DI, Bodary SC, Rosenberg S, Doyle MV, et al. Regulation of integrin function by the urokinase receptor. Science. 1996;273:1551–5.
84. Aguirre Ghiso JA, Kovalski K, Ossowski L. Tumor dormancy induced by downregulation of urokinase receptor in human carcinoma involves integrin and MAPK signaling. J Cell Biol. 1999;147:89–104.
85. Aguirre-Ghiso JA, Liu D, Mignatti A, Kovalski K, Ossow-ski L. Urokinase receptor and fibronectin regulate the ERK(MAPK) to p38(MAPK) activity ratios that determine carcinoma cell proliferation or dormancy in vivo. Mol Biol Cell. 2001;12:863–79.
86. Barkan D, Kleinman H, Simmons JL, Asmussen H, Kamaraju AK, Hoenorhoff MJ, et al. Inhibition of metastatic outgrowth from single dormant tumor cells by targeting the cytoskeleton. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6241–50.
87. Barkan D, El Touny LH, Michalowski AM, Smith JA, Chu I, Davis AS, et al. Metastatic growth from dormant cells induced by a col-I-enriched fibrotic environment. Cancer Res. 2010;70:5706–16.
88. Cho J, Lee HJ, Hwang SJ, Min HY, Kang HN, Park AY, et al. The interplay between slow-cycling, chemoresistant cancer cells and fibroblasts creates a proinflammatory niche for tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2020;80:2257–72.
89. Keeratichamroen S, Lirdprapamongkol K, Svasti J. Mechanism of ECM-induced dormancy and chemoresistance in A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;39:1765–74.
90. Di Martino JS, Nobre AR, Mondal C, Taha I, Farias EF, Fertig EJ, et al. A tumor-derived type III collagen-rich ECM niche regulates tumor cell dormancy. Nat Cancer. 2022;3:90–107.
91. Almog N, Ma L, Raychowdhury R, Schwager C, Erber R, Short S, et al. Transcriptional switch of dormant tumors to fast-growing angiogenic phenotype. Cancer Res. 2009;69:836–44.
93. Rouanne M, Adam J, Goubar A, Robin A, Ohana C, Louvet E, et al. Osteopontin and thrombospondin-1 play opposite roles in promoting tumor aggressiveness of primary resected non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:483.
94. Boyerinas B, Zafrir M, Yesilkanal AE, Price TT, Hyjek EM, Sipkins DA. Adhesion to osteopontin in the bone marrow niche regulates lymphoblastic leukemia cell dormancy. Blood. 2013;121:4821–31.
95. Parker AL, Cox TR. The role of the ECM in lung cancer dormancy and outgrowth. Front Oncol. 2020;10:1766.
96. Rodrigues LR, Teixeira JA, Schmitt FL, Paulsson M, Lindmark-Mansson H. The role of osteopontin in tumor progression and metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:1087–97.
97. Jiang Y, Zhang H, Wang J, Liu Y, Luo T, Hua H. Targeting extracellular matrix stiffness and mechanotransducers to improve cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:34.
98. Doue M, Okwieka A, Berquand A, Gorisse L, Maurice P, Velard F, et al. Carbamylation of elastic fibers is a molecular substratum of aortic stiffness. Sci Rep. 2021;11:17827.
99. Schrader J, Gordon-Walker TT, Aucott RL, van Deemter M, Quaas A, Walsh S, et al. Matrix stiffness modulates proliferation, chemotherapeutic response, and dormancy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 2011;53:1192–205.
100. Kondapaneni RV, Rao SS. Matrix stiffness and cluster size collectively regulate dormancy versus proliferation in brain metastatic breast cancer cell clusters. Biomater Sci. 2020;8:6637–46.
101. Anlas AA, Nelson CM. Soft microenvironments induce chemoresistance by increasing autophagy downstream of integrin-linked kinase. Cancer Res. 2020;80:4103–13.
102. Liu Y, Lv J, Liang X, Yin X, Zhang L, Chen D, et al. Fibrin stiffness mediates dormancy of tumor-repopulating cells via a Cdc42-driven Tet2 epigenetic program. Cancer Res. 2018;78:3926–37.
103. Sistigu A, Musella M, Galassi C, Vitale I, De Maria R. Tuning cancer fate: tumor microenvironment’s role in cancer stem cell quiescence and reawakening. Front Immunol. 2020;11:2166.
104. Butturini E, Carcereri de Prati A, Boriero D, Mariotto S. Tumor dormancy and interplay with hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:4305.
105. Ju S, Wang F, Wang Y, Ju S. CSN8 is a key regulator in hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and dormancy of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:168.
106. Ameri K, Jahangiri A, Rajah AM, Tormos KV, Nagarajan R, Pekmezci M, et al. HIGD1A regulates oxygen consumption, ROS production, and AMPK activity during glucose deprivation to modulate cell survival and tumor growth. Cell Rep. 2015;10:891–9.
107. Bildik G, Liang X, Sutton MN, Bast RC Jr, Lu Z. DIRAS3: an imprinted tumor suppressor gene that regulates RAS and PI3K-driven cancer growth, motility, autophagy, and tumor dormancy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022;21:25–37.
108. Sutton MN, Huang GY, Zhou J, Mao W, Langley R, Lu Z, et al. Amino acid deprivation-induced autophagy requires upregulation of DIRAS3 through reduction of E2F1 and E2F4 transcriptional repression. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11:603.
109. Wang L, Shang Z, Zhou Y, Hu X, Chen Y, Fan Y, et al. Autophagy mediates glucose starvation-induced glioblastoma cell quiescence and chemoresistance through coordinating cell metabolism, cell cycle, and survival. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:213.
110. Zhang M, Peng R, Wang H, Yang Z, Zhang H, Zhang Y, et al. Nanog mediated by FAO/ACLY signaling induces cellular dormancy in colorectal cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:159.
111. Dong X, Xue H, Mo F, Lin YY, Lin D, Wong NKY, et al. Modeling androgen deprivation therapy-induced prostate cancer dormancy and its clinical implications. Mol Cancer Res. 2022;20:782–93.
112. Kurppa KJ, Liu Y, To C, Zhang T, Fan M, Vajdi A, et al. Treatment-induced tumor dormancy through YAP-mediated transcriptional reprogramming of the apoptotic pathway. Cancer Cell. 2020;37:104–22.
113. Min M, Spencer SL. Spontaneously slow-cycling subpopulations of human cells originate from activation of stress-response pathways. PLoS Biol. 2019;17:e3000178.
114. Wagner EF, Nebreda AR. Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:537–49.
115. Adam AP, George A, Schewe D, Bragado P, Iglesias BV, Ranganathan AC, et al. Computational identification of a p38SAPK-regulated transcription factor network required for tumor cell quiescence. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5664–72.
116. Sosa MS, Parikh F, Maia AG, Estrada Y, Bosch A, Bragado P, et al. NR2F1 controls tumour cell dormancy via SOX9- and RARbeta-driven quiescence programmes. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6170.
117. Cai B, Chang SH, Becker EB, Bonni A, Xia Z. p38 MAP kinase mediates apoptosis through phosphorylation of BimEL at Ser-65. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:25215–22.
118. Zhuang S, Demirs JT, Kochevar IE. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates bid cleavage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and caspase-3 activation during apoptosis induced by singlet oxygen but not by hydrogen peroxide. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25939–48.
119. Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang Q, et al. p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Lett. 2014;344:174–9.
120. Kroeger H, Grimsey N, Paxman R, Chiang WC, Plate L, Jones Y, et al. The unfolded protein response regulator ATF6 promotes mesodermal differentiation. Sci Signal. 2018;11:eaan5785.
121. Fu Y, Li J, Lee AS. GRP78/BiP inhibits endoplasmic reticulum BIK and protects human breast cancer cells against estrogen starvation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2007;67:3734–40.
122. Schewe DM, Aguirre-Ghiso JA. ATF6alpha-Rheb-mTOR signaling promotes survival of dormant tumor cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:10519–24.
123. Gawrzak S, Rinaldi L, Gregorio S, Arenas EJ, Salvador F, Urosevic J, et al. MSK1 regulates luminal cell differentiation and metastatic dormancy in ER(+) breast cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:211–21.
124. Aman Y, Schmauck-Medina T, Hansen M, Morimoto RI, Simon AK, Bjedov I, et al. Autophagy in healthy aging and disease. Nat Aging. 2021;1:634–50.
125. Akkoc Y, Peker N, Akcay A, Gozuacik D. Autophagy and cancer dormancy. Front Oncol. 2021;11:627023.
126. Vera-Ramirez L. Cell-intrinsic survival signals. The role of autophagy in metastatic dissemination and tumor cell dormancy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;60:28–40.
127. Chen Y, Gibson SB. Three dimensions of autophagy in regulating tumor growth: cell survival/death, cell proliferation, and tumor dormancy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021;1867:166265.
128. Gupta A, Roy S, Lazar AJ, Wang WL, McAuliffe JC, Reynoso D, et al. Autophagy inhibition and antimalarials promote cell death in gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:14333–8.
129. Vera-Ramirez L, Vodnala SK, Nini R, Hunter KW, Green JE. Autophagy promotes the survival of dormant breast cancer cells and metastatic tumour recurrence. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1944.
130. Lu Z, Luo RZ, Lu Y, Zhang X, Yu Q, Khare S, et al. The tumor suppressor gene ARHI regulates autophagy and tumor dormancy in human ovarian cancer cells. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:3917–29.
131. Lu Z, Baquero MT, Yang H, Yang M, Reger AS, Kim C, et al. DIRAS3 regulates the autophagosome initiation complex in dormant ovarian cancer cells. Autophagy. 2014;10:1071–92.
132. Weiss A, Attisano L. The TGFbeta superfamily signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2013;2:47–63.
133. Bragado P, Estrada Y, Parikh F, Krause S, Capobianco C, Farina HG, et al. TGF-beta2 dictates disseminated tumour cell fate in target organs through TGF-beta-RIII and p38alpha/beta signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15:1351–61.
134. Yumoto K, Eber MR, Wang J, Cackowski FC, Decker AM, Lee E, et al. Axl is required for TGF-beta2-induced dormancy of prostate cancer cells in the bone marrow. Sci Rep. 2016;6:36520.
135. Kobayashi A, Okuda H, Xing F, Pandey PR, Watabe M, Hirota S, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 7 in dormancy and metastasis of prostate cancer stem-like cells in bone. J Exp Med. 2011;208:2641–55.
136. Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:505–18.
137. Rajbhandari N, Lin WC, Wehde BL, Triplett AA, Wagner KU. Autocrine IGF1 signaling mediates pancreatic tumor cell dormancy in the absence of oncogenic drivers. Cell Rep. 2017;18:2243–55.
138. Shimizu T, Sugihara E, Yamaguchi-Iwai S, Tamaki S, Koyama Y, Kamel W, et al. IGF2 preserves osteosarcoma cell survival by creating an autophagic state of dormancy that protects cells against chemotherapeutic stress. Cancer Res. 2014;74:6531–41.
139. Worster DT, Schmelzle T, Solimini NL, Lightcap ES, Millard B, Mills GB, et al. Akt and ERK control the proliferative response of mammary epithelial cells to the growth factors IGF-1 and EGF through the cell cycle inhibitor p57Kip2. Sci Signal. 2012;5:ra19.
140. Mercer TR, Mattick JS. Structure and function of long noncoding RNAs in epigenetic regulation. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013;20:300–7.
142. Nishikawa S, Dewi DL, Ishii H, Konno M, Haraguchi N, Kano Y, et al. Transcriptomic study of dormant gastrointestinal cancer stem cells. Int J Oncol. 2012;41:979–84.
143. Almog N, Briggs C, Beheshti A, Ma L, Wilkie KP, Rietman E, et al. Transcriptional changes induced by the tumor dormancy-associated microRNA-190. Transcription. 2013;4:177–91.
144. Vera-Ramirez L, Hunter KW. Tumor cell dormancy as an adaptive cell stress response mechanism. F1000Res. 2017;6:2134.
145. Schonthal AH. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: its role in disease and novel prospects for therapy. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:857516.
146. Wang M, Kaufman RJ. The impact of the endoplasmic reticulum protein-folding environment on cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:581–97.
147. Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:89–102.
148. Lee K, Tirasophon W, Shen X, Michalak M, Prywes R, Okada T, et al. IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genes Dev. 2002;16:452–66.
149. Maurel M, Chevet E, Tavernier J, Gerlo S. Getting RIDD of RNA: IRE1 in cell fate regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014;39:245–54.
150. Han J, Back SH, Hur J, Lin YH, Gildersleeve R, Shan J, et al. ER-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15:481–90.
151. Bartkowiak K, Kwiatkowski M, Buck F, Gorges TM, Nilse L, Assmann V, et al. Disseminated tumor cells persist in the bone marrow of breast cancer patients through sustained activation of the unfolded protein response. Cancer Res. 2015;75:5367–77.
152. Pommier A, Anaparthy N, Memos N, Kelley ZL, Gouronnec A, Yan R, et al. Unresolved endoplasmic reticulum stress engenders immune-resistant, latent pancreatic cancer metastases. Science. 2018;360:eaao4908.
153. Ranganathan AC, Zhang L, Adam AP, Aguirre-Ghiso JA. Functional coupling of p38-induced up-regulation of BiP and activation of RNA-dependent protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase to drug resistance of dormant carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1702–11.
154. Jaud M, Philippe C, Di Bella D, Tang W, Pyronnet S, Laurell H, et al. Translational regulations in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress in cancers. Cells. 2020;9:540.
155. Kehrl JH, Sinnarajah S. RGS2: a multifunctional regulator of G-protein signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;34:432–8.
156. Nguyen CH, Ming H, Zhao P, Hugendubler L, Gros R, Kimball SR, et al. Translational control by RGS2. J Cell Biol. 2009;186:755–65.
157. Zmijewski JW, Song L, Harkins L, Cobbs CS, Jope RS. Oxidative stress and heat shock stimulate RGS2 expression in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001;392:192–6.
158. Ota A, Sawai M, Sakurai H. Stress-induced transcription of regulator of G protein signaling 2 (RGS2) by heat shock transcription factor HSF1. Biochimie. 2013;95:1432–6.
159. Nguyen CH, Zhao P, Sobiesiak AJ, Chidiac P. RGS2 is a component of the cellular stress response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;426:129–34.
160. Park SY, Nam JS. The force awakens: metastatic dormant cancer cells. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52:569–81.
161. Adamski V, Hattermann K, Kubelt C, Cohrs G, Lucius R, Synowitz M, et al. Entry and exit of chemotherapeutically-promoted cellular dormancy in glioblastoma cells is differentially affected by the chemokines CXCL12, CXCL16, and CX3CL1. Oncogene. 2020;39:4421–35.
162. Hirano R, Okamoto K, Shinke M, Sato M, Watanabe S, Watanabe H, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages are major tumor-associated macrophage resources, contributing to early TNBC development, recurrence, and metastases. Commun Biol. 2023;6:144.
163. Liu H, Ling CC, Yeung WH, Pang L, Liu J, Zhou J, et al. Monocytic MDSC mobilization promotes tumor recurrence after liver transplantation via CXCL10/TLR4/MMP14 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:489.
164. Albrengues J, Shields MA, Ng D, Park CG, Ambrico A, Poindexter ME, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps produced during inflammation awaken dormant cancer cells in mice. Science. 2018;361:eaao4227.
165. Hast J, Schiffer IB, Neugebauer B, Teichman E, Schreiber W, Brieger J, et al. Angiogenesis and fibroblast proliferation precede formation of recurrent tumors after radiation therapy in nude mice. Anticancer Res. 2002;22:677–88.
166. Cho J, Min HY, Pei H, Wei X, Sim JY, Park SH, et al. The ATF6-EGF pathway mediates the awakening of slow-cycling chemoresistant cells and tumor recurrence by stimulating tumor angiogenesis. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12:1772.
167. Huang X, Wang L, Guo H, Zhang W, Shao Z. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals the regulative roles of cancer associated fibroblasts in tumor immune microenvironment of recurrent osteosarcoma. Theranostics. 2022;12:5877–87.
168. Bushnell GG, Deshmukh AP, den Hollander P, Luo M, Soundararajan R, Jia D, et al. Breast cancer dormancy: need for clinically relevant models to address current gaps in knowledge. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2021;7:66.
169. Heidrich I, Deitert B, Werner S, Pantel K. Liquid biopsy for monitoring of tumor dormancy and early detection of disease recurrence in solid tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023;42:161–82.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||