AbstractPurposeThe aim of this study was to evaluate the image quality of ultra-low-dose computed tomography (ULDCT) and its diagnostic performance in making a specific diagnosis of pneumonia in febrile neutropenic patients with hematological malignancy.
Materials and MethodsULDCT was performed prospectively in 207 febrile neutropenic patients with hematological malignancy. Three observers independently recorded the presence of lung parenchymal abnormality, and also indicated the cause of the lung parenchymal abnormality between infectious and noninfectious causes. If infectious pneumonia was considered the cause of lung abnormalities, they noted the two most appropriate diagnoses among four infectious conditions, including fungal, bacterial, viral, and Pneumocystis pneumonia. Sensitivity for correct diagnoses and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for evaluation of diagnostic accuracy were calculated. Interobserver agreements were determined using intraclass correlation coefficient.
ResultsOf 207 patients, 139 (67%) had pneumonia, 12 had noninfectious lung disease, and 56 had no remarkable chest computed tomography (CT) (20 with extrathoracic fever focus and 36 with no specific disease). Mean radiation expose dose of ULDCT was 0.60±0.15 mSv. Each observer regarded low-dose CT scans as unacceptable in only four (1.9%), one (0.5%), and three (1.5%) cases of ULDCTs. Sensitivity and area under the ROC curve in making a specific pneumonia diagnosis were 63.0%, 0.65 for reader 1; 63.0%, 0.61 for reader 2; and 65.0%, 0.62 for reader 3; respectively
IntroductionImmunocompromised patients with underlying hematologic malignancy are at increased risk of potentially fatal infection as a consequence of treatment-associated neutropenia [1]. The lungs are the most frequently involved organ for such infection [2]. According to a recent guideline established by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), chest radiograph is recommended for patients with respiratory signs and symptoms in order to rule out the presence of pneumonia [3]. The problem is that a chest radiograph frequently cannot depict the presence of lung abnormality at the early stage of pneumonia. Heussel et al. [4] demonstrated the presence of inflammatory pulmonary disease on computed tomography (CT) in more than 50% of febrile neutropenic patients who had normal chest radiographs. Hence, in daily practice, chest CT studies are recommended in patients with a risk for complicated pulmonary infection [5]; consequently, the rates of chest CT use have increased in febrile neutropenic patients [6].
On the other hand, although the immediate benefit to the individual patient can be substantial, the relatively high radiation doses associated with CT as compared with conventional radiography have raised health concerns [7]. A recent retrospective cohort study [8] showed an increase in leukemia and brain cancer rates in children who underwent multiple CT scans at ages younger than 15 years. In addition, thyroid glands, breast, and lungs are among the most cancer-susceptible organs in the body, and those organs are all included in chest CT. Therefore, although diagnostic information on lung abnormalities is needed in febrile neutropenic patients, CT radiation dose should be reduced as much as reasonably achievable [9].
An emerging method of reducing radiation exposure to populations requiring repeated imaging is the development of low-dose CT (LDCT) protocols [10-12]. Conversely, there has been concern over LDCT technique because the technique may cause increased image noise and thus degrade image quality. With recent rapid advancement of CT technology, however, tolerable-quality CT scans have been readily available via excessively small quantity of radiation exposure with an effective dose of less than one mSv (sub-mSv level, expressed as ultra-low-dose CT [ULDCT]) [13].
Currently, we are not precisely aware of the practical feasibility and usefulness of ULDCT for evaluation of patients with neutropenic fever. Therefore, the aim of our study was to assess the imaging quality of ULDCT and to evaluate the diagnostic performance of ULDCT technique in making a specific diagnosis in patients with hematologic malignancy and neutropenic fever.
Materials and Methods1. Study populationThis prospective study, conducted in a single-site, tertiary-care, and oncology center, was approved by our institutional review board (approval no. 2012-05-044), and written informed consent for the use of CT scan was obtained from all patients. Between July 2008 and March 2011, ULDCT studies were performed prospectively in all febrile neutropenic patients with a history of hematological malignancy. Clinical diagnosis of neutropenic fever was based on fulfillment of body temperature higher than 38 Celsius with absolute neutrophil count lower than 500. ULDCT was performed 2-3 days after development of neutropenic fever. Regardless of the suspicion of pneumonia, ULDCT was performed 2-3 days after development of neutropenic fever. According to the protocol of our hospital for care of hematologic malignancy patients since August 2006, if neutropenic fever is prolonged for two to three days, routine examination by ULDCT is performed in all patients because chest X-ray frequently fails to depict the presence of lung abnormality at the early stage of pneumonia.
2. CT scanning protocolULDCT scans were performed using a 16-detector row (LightSpeed16, GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI) scanner. Unenhanced CT images were obtained with the following parameters: detector collimation, 0.625 mm; field of view, 34.5 cm; beam pitch, 1.35 or 1.375; gantry speed, 0.6 second per rotation; 120 kVp; 25 mA; and section thickness, 1.25 mm, for transverse images. All imaging data were reconstructed using high- and low-spatial frequency reconstruction filters. Chest CT data were sent directly to a picture archiving and communication system (Path-Speed or Centricity 2.0, GE Healthcare, Mt. Prospect, IL), which displayed all image data on two monitors (1,536×2,048 matrix, eight-bit viewable grayscale, 60-foot-lambert [205.6 candela per square meter] luminescence). The monitors were used to view both mediastinal (width, 400 HU; level, 20 HU) and lung (width, 1,500 HU; level, –2,700 HU) window images.
3. Diagnostic evaluationCT images were assessed independently by three thoracic radiologists (K.S.L., J.W.M., K.E.S.; 30-, five-, and five-year experience in thoracic radiology, respectively) in a random order. They knew only that the patients had been referred for evaluation of neutropenic fever, and were unaware of all other clinical information. Before interpretation, an initial orientation session was held for all observers to review and become familiar with the descriptions of previously published data using articles containing other cases not included in the current study (Table 1) [4,14-16].
All ULDCT images were initially evaluated for their quality, based on soft-tissue contrast, the sharpness of tissue interfaces, and the conspicuity of focal abnormalities. The image quality was graded as excellent when images were comparable to those of standard-dose CT obtained for daily practice; acceptable when they were satisfactory for diagnostic evaluation; and unacceptable when they were unsatisfactory and additional imaging is needed for making an imaging diagnosis (Fig. 1).
Next, for each set of images, each observer recorded the presence or absence of lung parenchymal abnormality, and when abnormality was present, the observer also indicated the cause of the lung parenchymal abnormalities including infectious and noninfectious causes. If infectious pneumonia was considered the cause of lung abnormalities, they recorded the two most appropriate diagnoses among four infectious conditions, including fungal, bacterial, viral, and Pneumocystis pneumonia, and also recorded the confidence ratings for each diagnosis, ranging from 1% to 100%. The percentages given were used for receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for differential diagnosis of infectious pneumonia (Fig. 2).
According to a recent guideline established by the IDSA, all patients underwent chest X-rays. In addition, we reviewed the chest X-rays obtained before ULDCT in patients in whom abnormal findings were detected on ULDCT in order to determine the detection rate of chest X-rays and mortality of included patients because the purpose of ULDCT should be to reduce the incidence of respiratory failure and death.
4. Confirmation of diagnosisIf pneumonia was suspected on ULDCT, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was performed. To rule out other causes, either infection or not, we performed BAL for all included patients. BAL fluid analysis, including neutrophil or lymphocyte dominant, T cell subtype, and color of BAL fluid are important factors for differential diagnosis among infection, pulmonary hemorrhage, or drug reaction. Final diagnosis was made in each case by reviewing each patient's medical record and laboratory findings, including the following two weeks chest radiographs. An internal medicine physician (S.Y.P.) who subspecialized in respiratory medicine for eight years made an integrative confirmative diagnosis taking into account all clinical symptoms, laboratory test results, and response to treatments after discussion with more than three physicians, including an intensivist, pulmonologist, oncologist, intensive care unit fellow, and the physician in charge. If the decision was not concordant, we requested consultantation to the division of infectious disease. We validated precise diagnosis through serial follow up of chest X-ray, inflammatory markers such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein, and clinical symptoms of patients. Evidence of pneumonia on follow-up chest images and microorganisms detected during follow-up microbiologic studies were also regarded as documentation of pneumonia.
After the diagnoses were made, patients were categorized according to four groups based on having infectious pneumonia, noninfectious pulmonary disease, extrathoracic fever focus, and no remarkable chest CT without any specific lung fever focus. These categories kept completely grounded on clinical and microbiological diagnosis. First, the diagnosis of infectious pneumonia was made with the following clinical imaging and microbiological study results: a combination of lung lesions seen on ULDCT which were presumed to be possible for infectious focus, respiratory symptoms, specific pathogens identified from peripheral blood or BAL fluid analysis, or good response to antibiotic, antifungal, or antiviral treatments. The infectious pneumonia group was subdivided into four categories according to pathogens identified:bacterial,viral,fungal, and Pneumocystis jiroveci organisms. For example, in the case of cytomegalovirus (CMV) pneumonia, we checked CMV antigemia and treatment response. Second, diagnosis of noninfectious pneumonia was made on lung parenchymal lesions, which were deemed to be less responsible for infectious focus. In addition, the patients in this category did not show any response to antibiotic or antifungal treatment. Patients who had no abnormal lesions on ULDCT, no evidence of extrathoracic fever focus, no response to antibiotic, antifungal or antiviral treatments, and no new lesion on follow-up chest radiographs taken during two weeks after fever onset were categorized as having normal chest finding. Extrathoracic fever focus was elucidated by making a diagnosis of extrathoracic fever focus by disclosing definite evidence, such as catheter related infection, pseudomembranous colitis, or urinary tract infection.
5. Statistical analysisInterobserver agreements for imaging quality and differential diagnosis of ULDCT were estimated using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). ICC results were interpreted as follows: 0-0.2 indicates poor agreement; 0.3-0.4 indicates fair agreement; 0.5-0.6 indicates moderate agreement; 0.7-0.8 indicates strong agreement; and > 0.8 indicates almost perfect agreement. Sensitivities for the presence of lung abnormality on CT and correct diagnoses for infectious versus noninfectious causes were calculated using the standard definition. Sensitivity for differential diagnoses of infectious pneumonias was calculated based on per-patient which was a confirmed pathogen. In terms of assessment of mixed infection (more than one organism identified), the diagnosis was considered correct when two organisms recorded corresponded with any of one or two microbiologic organisms consequently identified. ROC analysis from recorded likelihood (percentages rendered for each diagnosis) for differential diagnosis of infectious pneumonia was also used for evaluation of diagnostic accuracy for infectious pneumonia. All analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics (ver. 19.0, IBM Co., Armonk, NY).
ResultsThe final study included 207 patients, and the clinical underlying diseases are summarized in Table 2. Of the 207 patients, 139 patients (67%) eventually proved to have infection, 12 patients (6%) had noninfectious causes, 36 patients (17%) had no remarkable chest CT, and the remaining 20 patients (10%) had extrathoracic infectious focus. Of 139 patients with infectious pneumonia, more than two pathogens were identified in 11 patients (8%). Therefore, a total of 150 pathogens were identified (139+11 pathogens). Bacterial, fungal, viral, and Pneumocystis jiroveci organisms accounted for 48 (35%), 55 (40%), 42 (30%), and four (2.9%) of 150 pathogens, respectively. In 12 patients with noninfectious cause for lung abnormalities, final diagnoses were reached by biopsy (graft-versus-host disease, relapsing leukemia, and all-trans-retinoic acid syndrome), observing the clinical course (overhydration in four patients, drug toxicity in two patients improved after drug off), and BAL (diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in three patients). In 36 patients with no remarkable chest CT, the absence of lung abnormality was confirmed by the absence of lung lesions on both clinico-laboratory data and follow-up chest radiographs for two weeks after the no remarkable chest CT. Final diagnoses in 20 patients of the extrathoracic fever focus group were eight urinary tract infections, ten catheter-related infections, and two pseudomembranous colitis.
1. Image quality of ULDCTMedian body mass index (BMI) was 22 kg/m2 , which belonged to the normal weight category (18.5-24.9 kg/m2). Out of 207 patients, 29 patients (14%) fell into the overweight category (25-29.9 kg/m2). Body weight and BMI of each patient were within average range. Most patients were very cachexic due to underlying malignancy, so that there was no evidence that it had any effect on the image quality.
Mean radiation exposure dose of ULDCT was 0.60±0.15 mSv, and was approximately one twelfth of the effective dose of conventional chest CT (7.0 mSv) [17]. Image quality assessment and interobserver agreement by three observers are shown in Table 3. Unacceptable image quality was rendered in only four (1.9%), one (0.5%), and three (1.5%) ULDCTs; other scans were regarded as excellent or acceptable quality.
2. Diagnostic performanceThe presence or absence of lung abnormality was correctly determined in 183 of 207 patients (88.4%), 169 (81.6%), and 189 (91.3%), respectively, by three observers, and interobserver agreement for the presence of lung abnormality was 0.85. When counting the first diagnosis recorded (infectious versus noninfectious), overall correct diagnoses including infectious and noninfectious causes for lung abnormalities were made in 105 of 151 patients (69.5%) with lung abnormality, 104 (68.9%), and 108 (71.5%), respectively, by three observers.
Sensitivity and area under the ROC curve for correct diagnosis of infectious pneumonia were 63% (95 of 150 pathogens) with 0.65 for reader 1; 63%, 0.61 (91 of 150) for reader 2; and 65%, 0.62 (93 of 150) for reader 3; respectively (Table 4). The mean percentages of correct diagnoses made by at least two of three radiologists were all more than 60% for four categories. Three radiologists reached unanimous agreement on the correct diagnosis for infectious pneumonia (as for organisms) in 65 cases (47%).
Compared with ULDCT, among the 151 patients (139 patients of infectious cause and 12 patients of noninfectious case) in whom lung abnormality was detected on ULDCT, the detection rate of lung parenchymal opacity through chest X-ray was only 38.5% (58 patients), which is much lower than that for ULDCT. Of these, the mortality rate in patients with infectious pneumonia who died within one month was 5% (7/139 patients).
DiscussionPneumonias represent the most unfavorable infectious complications occurring during the course of neutropenia in patients with cancer. The incidence of pneumonia in high-risk patients (e.g., patients with acute leukemias) is 17% [2] to 24% [18], and their clinical response to broad spectrum antibiotic therapy—eventually supplemented by antifungal treatment active against Aspergillus species—is 60% to 65%, whereas the infection-related fatality rate in these patients may be as high as 38% [18]. Thus, lung infections are associated with significant prognostic deterioration in patients with cancer [19]. However, efforts to identify the etiology of pneumonia in febrile neutropenic patients by use of invasive techniques have not clearly improved. The diagnostic yield of conventional chest radiography is poor [20,21] and the diagnostic yield of BAL fluid procedures is controversially debated [21].
Although recent various nonculture based sensitive tests for pathogen identification, such as serum galactomannan test [22] or CMV antigen titer test, enable increased diagnostic accuracy of pulmonary infection, these tests have poorer sensitivity in non-neutropenic patients and in patients receiving mold-active prophylaxis. In addition, false-positive results due to cross reactivity during administration of piperacillin-tazobactam, which is used in many hematology units as the front-line anti-Pseudomonas antibiotics for febrile neutropenia, can also be a problem [3,6]. Therefore, many patients with neutropenic fever and normal chest radiographic findings may undergo chest CT to determine whether or not lung parenchyma abnormalities are present, and for consideration of a particular pathogen, even though the radiologic manifestations of pneumonia are not specific enough to make a differential diagnosis of infection from other causes of lung abnormality.
Meanwhile, prognosis is significantly influenced by early identification of lung infiltrates by means of chest CT, because it leads to earlier commencement of therapy and enables selection of better-tolerated, effective, and safe treatment options [16]. Above all, pneumonia in general appears initially as subtle lesions which are not detectable on chest radiograph, and in some patients with neutropenia or immunocompromised state, the pneumonia shows rapid progression. Therefore, prognosis of febrile neutropenic patients is determined by early identification of the underlying microorganisms and the timely start of specific antimicrobial drug therapy. In addition, chest CT may be used to monitor patient response to therapy [14]. Repeated CT scans at short-term intervals may be necessary when pneumonia during a neutropenic period may progress rapidly to respiratory failure.
In our study, ULDCT showed good image quality with almost perfect agreement and highly acceptable performance for the diagnosis of pulmonary infection. Results of our study suggest that ULDCT enables as high diagnostic sensitivity for pulmonary infection in patients with neutropenic fever as CT of standard dose [16]. In addition, we identified definite superiority in detection of ULDCT compared with chest X-ray.
Body weight and BMI might affect the CT image [23]. However, in our study, the body weight and BMI of each patient were within average range, and were not a concern.
According to Heussel et al. [24], in 70 (48%) of 146 cases, findings on chest radiographs were normal, whereas findings on thin-section CT scans were suggestive of pneumonia. More importantly, the probability of development of pneumonia was less than 15% among those with negative CT results. CT information showing that lungs are probably not involved with inflammatory/infectious disease can be very important for the referring hematologist, because reasons for fever and its relation to pulmonary infection should be readily clarified.
We designed this study prospectively in order to investigate the diagnostic value of ULDCT in clinical practice. And, in more than 60% of patients, infectious pathogens could be predicted, thus demonstrating clinical relevance of performing ULDCT in patients with fever and hematologic malignancy. Therefore, ULDCT could perhaps be considered as a study of choice in the context of assessing pulmonary infection in febrile neutropenic patients, because this technique allowed a reduction of radiation dose by up to 91%. Similarly, Patsios et al. [11] compared LDCT with chest radiography in assessment of febrile hematologic malignancy patients. Overall, 31 of 40 chest radiographs (77.5%) were abnormal, whereas LDCT was helpful in detection of lung abnormalities in 38 patients (95.0%), and the additional information provided by LDCT led to an alteration in the clinical management methods in 11 of 40 patients (27.5%).
A large well-designed epidemiologic study has clearly shown that the individual risks of radiation exposure in diagnostic imaging are small but real [8]. Therefore, it seems to be no longer tenable to claim that CT risks are “too low to be detectable and may be non-existent” [3]. Given the current level of scientific uncertainty regarding radiation risk at low-dose level, it may be appropriate to act on the assumption that such risks are real, as this conservative approach is unlikely to underestimate patient risks [21]. Our study has demonstrated a significant reduction of effective radiation dose without abandonment of the image quality. ULDCT contributed to the appropriate treatment for neutropenic patients, at a relatively early stage. By using ULDCT, we might expect a better survival rate in febrile neutropenic patients with hematologic malignancy.
The current study has several limitations. First, invasive diagnostic procedures for histopathologic or microbiologic confirmation were not performed in all patients. However, even with surgical lung biopsy the definite diagnosis could not be made in a certain percentage of patients in whom identifiable abnormalities were observed on CT or chest radiography. Also in our study, diagnoses for lung abnormalities were made by integrating clinical, laboratory, imaging, microbiologic, or histopathologic findings. Second, because this study was conducted prospectively before the clinical use of state-of-the-art dose reduction techniques such as adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR) or model-based iterative reconstruction [25], such new techniques could not be applied in our study. If these techniques could have been applied, the lowest thus more mitigated radiation-dose CT images might have been produced and used for image interpretation. However, there has still been debate regarding the image quality of ASIR-applied image, particularly for interstitial lung lesions or ground-glass opacities due to spatial resolution and edge sharpness [23]. In addition, we did not obtain the standard dose CT simultaneously for direct comparison with image quality because our concern was the precise impact on clinical decision. The other reason was the ethical concern of increased radiation exposure by double scanning. We also worried about a higher radiation exposure dose of ULDCT compared with chest X-ray. We did the best we could to reduce the radiation dose even approximately one twelfth of the effective dose of conventional chest CT (7.0 mSv). And, we thought that reduction of mortality due to early detection of fever focus is more important than radiation hazard.
ConclusionIn conclusion, ULDCT, with a very low level of patient radiation dose, provides acceptable image quality and provides ready and reasonably acceptable diagnostic information for lung abnormalities, particularly for diagnosis of pulmonary infection in febrile neutropenic and hematologic-malignancy patients.
AcknowledgmentsThe authors are grateful to the study participants and observers at the Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center.
Fig. 1.Representative figures for assessment of image quality. (A) Excellent image quality. (B) Acceptable image quality. (C) Unacceptable image quality. 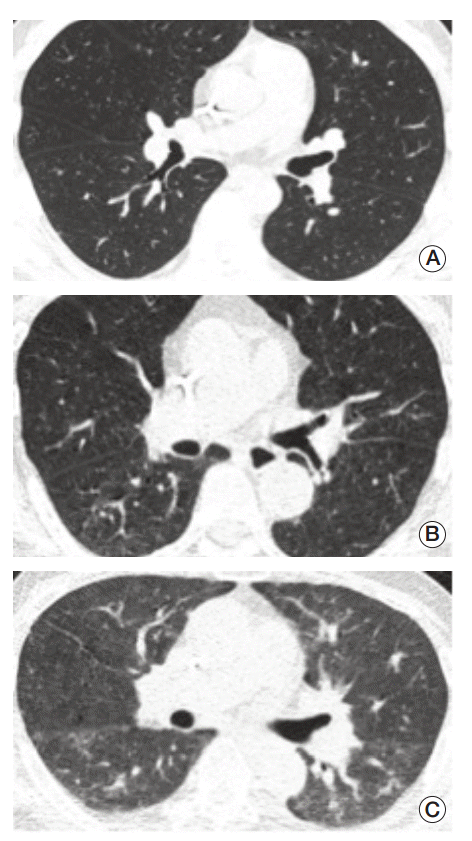
Fig. 2.Representative cases for infectious pneumonia. (A) Transverse ultra-low-dose computed tomography (ULDCT) scan in a patient with Aspergillus infection shows a nodule surrounded by a halo of ground-glass opacity in the left lower lobe (arrow). All three observers reached a consensus as an excellent image quality level. (B) Transverse ULDCT scans in a patient with Pneumocystis pneumonia show bilateral patchy areas of ground-glass opacity (arrows). All three observers reached a consensus as an acceptable image quality level. (C) Transverse and coronal ULDCT scans in a patient with streptococcal pneumonia show consolidation involving the posterior basal segment of the right lower lobe (arrows). All three observers reached a consensus as an acceptable image quality level. (D) Transverse ULDCT scans in a patient with coronavirus infection show multiple centrilobular nodules (arrowheads) and bilateral areas of lobular consolidation of peribronchial distributions (arrows). All three observers reached a consensus as an unacceptable image quality level. 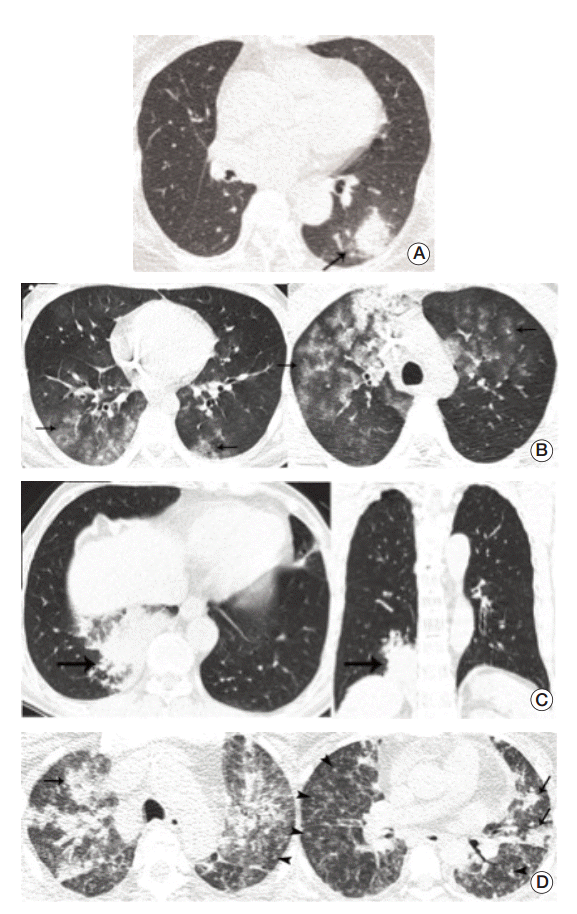
Table 1.Radiological appearance of various infectious and noninfectious lung diseases in neutropenic hosts
Table 2.Patients' characteristics (n=207)
BMI, body mass index; CT, computed tomography; BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; AML, acute myelogenous leukemia; ALL, acute lymphocytic leukemia; CML, chronic myelogenous leukemia; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; MDS, myelodysplastic syndromes; CT, computed tomography. Table 3.Grading of imaging quality for adequacy of diagnosis
Table 4.Diagnostic accuracy
References1. de Naurois J, Novitzky-Basso I, Gill MJ, Marti FM, Cullen MH, Roila F, et al. Management of febrile neutropenia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann Oncol. 2010;21 Suppl 5:v252-6.
2. Maschmeyer G, Link H, Hiddemann W, Meyer P, Helmerking M, Eisenmann E, et al. Pulmonary infiltrations in febrile patients with neutropenia: risk factors and outcome under empirical antimicrobial therapy in a randomized multicenter study. Cancer. 1994;73:2296–304.
3. Freifeld AG, Bow EJ, Sepkowitz KA, Boeckh MJ, Ito JI, Mullen CA, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer: 2010 update by the infectious diseases society of america. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:e56–93.
4. Heussel CP, Kauczor HU, Heussel GE, Fischer B, Begrich M, Mildenberger P, et al. Pneumonia in febrile neutropenic patients and in bone marrow and blood stem-cell transplant recipients: use of high-resolution computed tomography. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:796–805.
5. Rizzi EB, Schinina V, Gentile FP, Bibbolino C. Reduced computed tomography radiation dose in HIV-related pneumonia: effect on diagnostic image quality. Clin Imaging. 2007;31:178–84.
6. Stanzani M, Battista G, Sassi C, Lewis RE, Tolomelli G, Clissa C, et al. Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography for diagnosis of invasive mold diseases in patients with hematological malignancies. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:610–6.
7. Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography: an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2277–84.
8. Pearce MS, Salotti JA, Little MP, McHugh K, Lee C, Kim KP, et al. Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2012;380:499–505.
9. Hendee WR, O'Connor MK. Radiation risks of medical imaging: separating fact from fantasy. Radiology. 2012;264:312–21.
10. Kalra MK, Maher MM, Toth TL, Hamberg LM, Blake MA, Shepard JA, et al. Strategies for CT radiation dose optimization. Radiology. 2004;230:619–28.
11. Patsios D, Maimon N, Chung T, Roberts H, Disperati P, Minden M, et al. Chest low-dose computed tomography in neutropenic acute myeloid leukaemia patients. Respir Med. 2010;104:600–5.
12. Takahashi M, Maguire WM, Ashtari M, Khan A, Papp Z, Alberico R, et al. Low-dose spiral computed tomography of the thorax: comparison with the standard-dose technique. Invest Radiol. 1998;33:68–73.
13. Udayasankar UK, Li J, Baumgarten DA, Small WC, Kalra MK. Acute abdominal pain: value of non-contrast enhanced ultra-low-dose multi-detector row CT as a substitute for abdominal radiographs. Emerg Radiol. 2009;16:61–70.
14. Caillot D, Couaillier JF, Bernard A, Casasnovas O, Denning DW, Mannone L, et al. Increasing volume and changing characteristics of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis on sequential thoracic computed tomography scans in patients with neutropenia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:253–9.
16. Heussel CP, Kauczor HU, Ullmann AJ. Pneumonia in neutropenic patients. Eur Radiol. 2004;14:256–71.
17. Mayo JR, Aldrich J, Muller NL; Fleischner Society. Radiation exposure at chest CT: a statement of the Fleischner Society. Radiology. 2003;228:15–21.
18. Rossini F, Verga M, Pioltelli P, Giltri G, Sancassani V, Pogliani EM, et al. Incidence and outcome of pneumonia in patients with acute leukemia receiving first induction therapy with anthracycline-containing regimens. Haematologica. 2000;85:1255–60.
19. Quadri TL, Brown AE. Infectious complications in the critically ill patient with cancer. Semin Oncol. 2000;27:335–46.
20. Donowitz GR, Harman C, Pope T, Stewart FM. The role of the chest roentgenogram in febrile neutropenic patients. Arch Intern Med. 1991;151:701–4.
21. Korones DN, Hussong MR, Gullace MA. Routine chest radiography of children with cancer hospitalized for fever and neutropenia: is it really necessary? Cancer. 1997;80:1160–4.
22. Neofytos D. Chest computed tomography versus serum galactomannan enzyme immunoassay for the diagnosis of probable invasive aspergillosis: to be decided. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:1281–3.
23. Prakash P, Kalra MK, Digumarthy SR, Hsieh J, Pien H, Singh S, et al. Radiation dose reduction with chest computed tomography using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique: initial experience. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2010;34:40–5.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||