Introduction
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with activating epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation treated with either a first- or second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) can experience treatment failure, most commonly by acquiring an additional genomic alteration in EGFR T790M [1]. Lazertinib (YH25448) is a potent irreversible third-generation EGFR TKI that targets both T790M and activating EGFR mutation with high penetration to the blood-brain barrier. Lazertinib showed promising anti-tumor efficacy with a 57% overall response rate and 9.7-month median progression-free survival in EGFR T790M-positive patients [2]. However, there is no previous report showing the mechanism of tumor resistance acquisition to lazertinib. In this case report, we conducted deep-targeted sequencing of resistant tumor samples and established patient-derived cell lines (PDC) from a patient treated with lazertinib to elucidate the underlying genomic alteration associated with resistance.
Case Report
A 38-year-old current male smoker presented with stage 4, cT1bN3M1b, NSCLC adenocarcinoma. Informed consent was received under supervision of institutional review board (SMC 2011-10-054-034). The patient was shown to harbor an EGFR exon 19 deletion using real-time polymerase chain reaction from the initial biopsy sample obtained from the mediastinal lymph node. Afatinib was administered as a first-line treatment and showed very good partial response with 7.1 months of progression-free survival. After first-line EGFR TKI failure, a second biopsy from the newly progressed metastatic lymph node showed acquired EGFR T790M mutation. As a subsequent treatment, the patient received lazertinib as a part of a clinical trial (NCT03046992, YH25448-201). However, after 6.2 months of partial response to lazertinib, the patient developed malignant ascites, suggesting peritoneal seeding due to resistance.
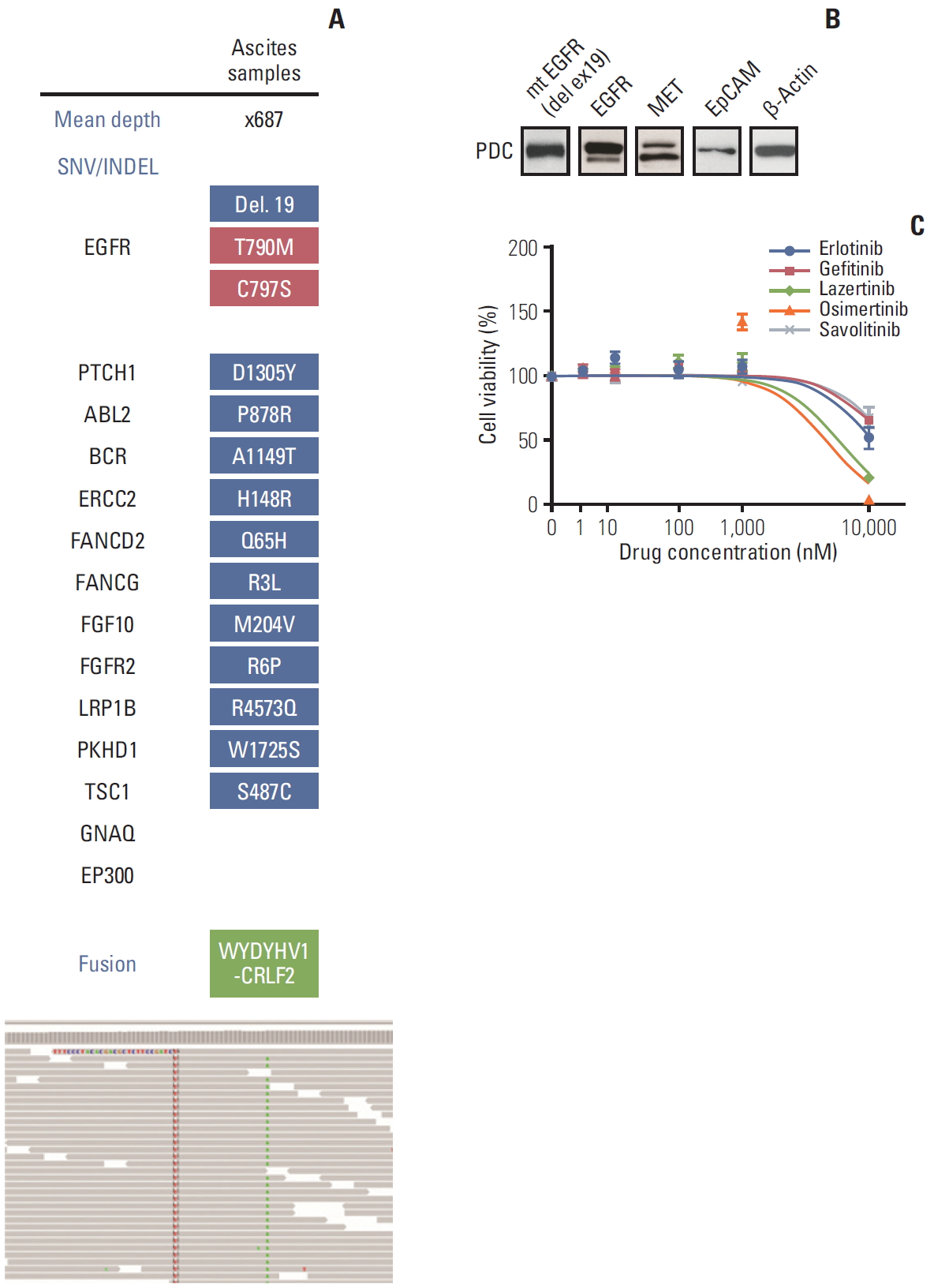
Deep-targeted sequencing (CancerSCAN [3]) of ascites samples demonstrated acquired EGFR C797S mutation in cis, variant allele frequency (VAF) of 9.4%, EGFR T790M (VAF of 3.5%), and EGFR exon 19 deletion (VAF 9.2%) (Fig. 1A). PDCs established from the same ascites sample showed EGFR exon 19 deletion (Fig. 1B). Cell viability of PDCs showed resistance to first- and third-generation EGFR TKIs including erlotinib, gefitinib, lazertinib, and osimertinib or the c-Met inhibitor savolitinib (Fig. 1C).
Discussion
Diverse resistance mechanisms to third-generation EGFR TKI have been reported including loss of T790M, acquisition of EGFR C797S mutation, c-Met amplification, activation of other bypass tract, or small cell lung cancer transformation. Among them, EGFR C797S/T790M mutation is the most frequently observed, accounting for 20%-30% of cases. It is of note that tumors acquiring an additional mutation of EGFR C797X maintain the original EGFR T790M mutation [4]. In this report, we present the first clinical case of new EGFR C797S/T790M mutation in a patient who failed lazertinib. Further validation with a large number of patients and new treatment strategies to overcome this resistance mutation are warranted.