AbstractPurposeExtranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL) is a rare subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and asparaginase-based regimens are the best first-line treatments. Data on the role of specific circulating lymphocyte subsets in the progression of ENKTL are limited. The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical correlation and distribution of circulating absolute CD4+ T-cell counts (ACD4Cs) in ENKTL.
Materials and MethodsWe retrospectively searched medical records for 70 newly diagnosed ENKTL patients treated with pegaspargase-based regimens. Comparison of ACD4Cs as a continuous parameter in different groups was calculated. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to assess prognostic factors for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS).
ResultsStage III/IV, B symptoms, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, monocytopenia, high-intermediate and high risk International Prognostic Index (IPI) and Korean Prognostic Index (KPI), high risk Prognostic Index of Natural Killer Lymphoma (PINK), and lower lymphocytes were significantly associated with low ACD4C at diagnosis. With a median follow-up time of 32 months, patients who had an ACD4C < 0.30×109/L had a worse OS. Median OS was 11 months and median PFS was 5 months in the low ACD4C cohort. There were significant differences in both OS and PFS between the two cohorts. Moreover, multivariate Cox analysis identified ACD4Cs as an independent predictor for OS and PFS.
IntroductionExtranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL) is a rare subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), with distinct epidemiological and clinicopathological features. In China, ENKTL accounts for 5.26%-16.0% of all NHL and is higher than in Western countries [1-4]. Comprehensive data on clinicopathologic features and prognostic factors of ENKTL have been well presented. The prognosis of ENKTL is variable, with some patients responding well to therapy and others dying of disseminated disease despite highly effective asparaginase-containing treatment. Significantly unfavorable prognostic factors include age, elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), B symptoms, higher performance status (PS) score, advanced stage disease, invasion of extranasal sites, and high circulating Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA levels, which focus mainly on the clinical characteristics of ENKTL; the prognostic significance of the International Prognostic Index (IPI), the Korean Prognostic Index (KPI), and the Prognostic Index of Natural Killer Lymphoma (PINK) have been verified in many studies [5,6].
ENKTL patients have immune function disorders, which are involved in the pathogenesis and progression of disease. In fact, changes in the tumor microenvironment and host immunity often occur and play important roles in disease progression of some subtypes of lymphoma. CD4+ T cells are critical to maintain EBV-specific effector and central memory T lymphocytes, which might be an important factor during the progression of lymphomas. Peng et al. [7] showed that the density of CD4+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) was negatively correlated with IPI and KPI scores, which suggested that CD4+ TILs was decreased in high-risk patients with ENKTL. CD8+ T cells also play an important role in controlling and eliminating EBV-infected cells and are related to antitumoral and antiviral immune effects. Furthermore, T cells could be used as therapeutic targets in ENKTL patients. A recent trial showed that relapsed/refractory ENKTL patients resistant to L-asparaginase-based regimens achieved an excellent response by inducing T-cell cytotoxicity in lymphoma cells [8]. Therefore, it is important to evaluate the host immune response of patients with ENKTL.
Several retrospective studies have demonstrated that a decreasing absolute lymphocyte counts (ALCs) is an unfavorable prognostic index for ENKTL, while an increasing ALCs is a favorable prognostic index. However, treatment is heterogeneous and many patients received an inferior regimen like anthracycline-containing treatment [9,10]. Data are limited with respect to the role of specific circulating lymphocyte subsets in the progression of ENKTL patients, especially those treated with asparaginase-containing regimens [11,12]. Recent studies have suggested that there was a negative prognostic impact associated with low absolute CD4+ T-cell counts (ACD4Cs) in peripheral blood from follicular lymphoma (FL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients [13,14]. Since the pathogenesis of ENKTL is strongly associated with immune cells infected with EBV, we speculated that host immune status might be linked to the prognosis of ENKTL. Few studies have investigated the role of host immunity in patients with ENKTL. Analysis of the role of circulating T-cell subsets may provide useful information for gaining a better understanding of ENKTL. Here, we assessed the distribution of ACD4Cs and investigated its association with clinical features and survival outcome in ENKTL.
Materials and Methods1. Case selection and clinical characteristicsWe retrospectively searched the medical records and identified 70 newly diagnosed ENKTL patients treated with pegaspargase-based regimens at the Department of Hematology at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (Jiangsu Province Hospital) from August 1, 2009, to May 31, 2016. The ENKTL diagnosis was based on clinical, morphologic, and immunophenotypic information, according to World Health Organization (WHO) classification criteria [15]. Patients with aggressive NK cell lymphoma/leukemia, blastic NK cell lymphoma/leukemia, EBV-negative lymphoma/leukemia by in situ hybridization (ISH), previously treated ENKTL, or ENKTL not treated with pegaspargase-based regimens were excluded from the present study. Patient clinical characteristics were obtained from medical records, including age, sex, disease sites, PS, B symptoms, Ann Arbor stage, lymph node involvement, and complete blood counts (CBCs). 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography, and computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging examinations were performed for staging at diagnosis and evaluating efficacy.
2. Immunophenotypic analysisPathologic slides from tissue blocks, bone marrow aspirate smears, and biopsy specimens were reviewed. Immunohistochemistry was performed using formalin-fixed, paraffinembedded 4-μm-thick tissue sections. The antigen retrieval technique was performed as needed. Monoclonal antibodies used included CD2, cytoplasmic CD3, CD4, CD5, CD7, CD8, CD20, CD30, CD56, T-cell intracellular antigen (TIA-1), perforin, granzyme B, and Ki-67. ISH analysis for EBV-encoded RNA (EBER) was performed for all cases. Flow cytometry (FCM) immunophenotypic analysis was performed on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton-Dickinson, San Jose, CA). Murine anti-human monoclonal antibodies from BD Biosciences were used, including anti‒CD3-fluorescein isothiocyanate, anti–CD4-phycoerythrin (PE), anti–CD8-allophycocyanin (APC), anti‒CD16-PE, and anti–CD56-APC. Mature red blood cells were lysed using Tris-NH4Cl solution. Fresh peripheral blood samples were mixed with fluorescent labeled antibodies for 15 minutes in the dark at room temperature. Lymphocytes were delineated using forward-scatter and side-scatter dot plots. The lymphocyte population was gated using CD45 expression and side scatter. CellQuest software was used to analyze the data. PBMC specimens were analyzed using CBC and FCM to determine the percentages of lymphocyte subsets and calculate absolute CD4+ T cell counts.
3. TreatmentsPegaspargase-based chemotherapy regimens with or without radiotherapy, including P-CHOP (pegaspargase, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), P-CHOEP (CHOP, pegaspargase, and etoposide), P-EPOCH (pegaspargase, etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin), PMED (pegaspargase, methotrexate, etoposide, and dexamethasone), DMIPE (dexamethasone, methotrexate, ifosfamide, pegaspargase, and etoposide), or P-GemOX (pegaspargase, gemcitabine, and oxaliplatin) were administrated to all patients. Patients received two to six cycles of chemotherapy as initial treatment. Radiotherapy doses used in chemoradiotherapy was no more than 54 Gy (range, 40 to 54 Gy).
4. Statistical analysisStatistical analyses were performed with SPSS ver. 13.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). Comparison of ACD4Cs as a continuous parameter in different groups was calculated using the Mann–Whitney U test for unpaired samples. Cutoff values were determined using the X-tile program (http://www.tissuearray.org/rimmlab/), which identified cutoffs with minimum p-values from log-rank analysis in terms of overall survival (OS) [16]. OS was defined as the length of time from the initial diagnosis to the time of death from any cause or last contact. Progression-free survival (PFS) was defined as the length of time from the initial diagnosis to the time of first occurrence of progression after response, or last contact. OS and PFS were analyzed using the method of Kaplan-Meier and compared using the log-rank test. Univariate analysis was used to assess prognostic factors for OS and PFS. The Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to estimate the hazard ratio (HR) and confidence interval (CI) of significant variables in multivariate analysis. p-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results1. Patient characteristics, and associations between ACD-4Cs and clinical featuresWe investigated 70 untreated patients with ENKTL, including 55 men (78.6%) and 15 women (21.4%) (male to female ratio, 3.7:1). The median age of patients at the time of diagnosis was 47 years (range, 14 to 84 years), and 21 (30.0%) of them were more than 60 years old. Forty-one patients (58.6%) were diagnosed at stage I/II with a median ACD4C of 0.50×109/L, versus 29 (41.4%) at stage III/IV with a median ACD4C of 0.36×109/L (p=0.029). B symptoms were observed in 42 patients (60.0%) with a median ACD4C of 0.39×109/L, which was lower than in 28 patients (40.0%) without B symptoms (p=0.033). Fifty-eight patients (82.9%) with primary upper aerodigestive tract diseases were designated as nasal ENKTL, while 12 (17.1%) patients were diagnosed with extranasal presentation of skin, gastrointestinal tract, lung, or penis involvement. There was no significant difference in median ACD4Cs between nasal and extranasal ENKTL (p=0.377). Median ACD4Cs in cases with normal LDH (n=46, 65.7%) was higher than that in cases with elevated LDH (n=24, 34.3%) (0.52×109/L vs. 0.30×109/L, p=0.001). Twenty-two patients (31.4%) were in the high-intermediate or high-risk groups evaluated using IPI. A KPI score greater than two was determined in 38 patients (54.3%). Patients with low to low-intermediate risk of IPI and KPI both had significantly higher median ACD4Cs than those in the high-intermediate or high-risk groups. According to the newest scoring system, a PINK score of greater than one was determined in 32 cases (45.7%) with a median ACD4C of 0.33×109/L, versus 0.47×109/L in the low and intermediate risk groups (p=0.015). The median ACD4C at diagnosis was 0.29×109/L in the group with decreasing monocytes, lower than that which was found in the group with a normal level of monocytes (p=0.009). Patients with normal levels of neutrophils, hemoglobin, and platelets had higher ACD4Cs than patients with abnormal results, although statistical significance was not reached (Table 1).
2. Associations between ACD4Cs and survivalAll patients were treated with pegaspargase-based regimens, including chemotherapy alone (35.7%, 25/70) and chemoradiotherapy (64.3%, 45/70). The median number of cycles for the first-line regimen was four cycles. Two patients received hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), including an upfront autologous HSCT and a salvage allogeneic HSCT. With a median follow-up of 32 months (range, 5 to 80 months), 23 patients (32.9%) died. The 1- and 3-year OS rates were 71.8% and 65.2%, respectively, while the 1-and 3-year PFS rates were 65.0% and 58.5%, respectively. In order to further analyze the clinical significance of ACD4Cs, we used the X-tile program to identify the cutoff value of ACD-4Cs as 0.30×109/L with the minimum p-values from log-rank analysis in terms of OS. Patients were divided into ACD4Cs ≥ 0.30×109/L and ACD4Cs < 0.30×109/L groups. There were significant differences in both OS (p < 0.001) (Fig. 1) and PFS (p < 0.001) (Fig. 2) between the ACD4Cs ≥ 0.30×109/L group and the ACD4Cs < 0.30×109/L group. In the ACD4Cs ≥ 0.30×109/L group, median OS and PFS were not reached. The 1-and 3-year OS rates were 84.3% and 77.8%, respectively, while the 1- and 3-year PFS rates were 82.7% and 72.6%, respectively. In the ACD4Cs < 0.30×109/L group, patients had worse survival. The median OS time was only 11 months and the median PFS was 5 months. The 1- and 3-year OS rates were 47.8% and 30.7%, respectively, while the 1- and 3-year PFS rates were 34.8% and 30.4%, respectively. The prognostic value of ACD4Cs was separately analyzed according to stage as well. In early stage (stage I/II) ENKTL patients, ACD4Cs < 0.30×109/L signified shorter survival for both OS (p=0.001) and PFS (p=0.009) (Fig. 3). While in advanced stage (stage III/IV) patients, ACD4Cs merely showed poor prognostic value in PFS (p=0.046) (Fig. 4).
3. Prognostic factorsThe correlation between clinical characteristics and survival was evaluated using univariate and multivariate analyses. In univariate analysis, results demonstrated that low ACD4Cs (p < 0.001), poor PS (p=0.028), stage III/IV (p=0.001), regional lymphadenopathy (p=0.020), primary extranasal presentation (p=0.012), high risk PINK (p=0.001), high and high-intermediate risk IPI (p=0.001), and KPI (p=0.003) were correlated with a worse OS. In terms of PFS, patients with low ACD4Cs (p < 0.001), stage III/IV (p < 0.001), regional lymphadenopathy (p=0.006), primary extranasal presentation (p=0.039), high risk PINK (p=0.001), high and high-intermediate risk IPI (p=0.003), and KPI (p=0.001) had inferior survival. Our findings also demonstrated that there was no correlation between absolute CD8+ T cell counts (ACD8Cs) and survival (Table 2). PINK is considered to be the most important prognostic model for predicting survival in patients with ENKTL, which includes prognostic factors confirmed in univariate analysis such as age, stage, distant lymph nodes, and extranasal involvement. Therefore, we put age, stage, distant lymph nodes, extranasal involvement and ACD4Cs into the multivariate model. In multivariate Cox analysis, low ACD4Cs maintained their prognostic value for OS (HR, 2.992; 95% CI, 1.180 to 7.585; p=0.021) and PFS (HR, 2.761; 95% CI, 1.201 to 6.345; p=0.017) (Table 3).
DiscussionImmune function disorders have been observed in several types of tumors. Both pathogenesis and prognosis have a significant correlation with the tumor microenvironment and host immunity. The tumor microenvironment has been shown to be a prognostic marker in certain types of lymphomas [17-20]. Regarding host immunity, several studies correlating circulating immune populations of peripheral blood cells with outcome in B-cell lymphoma have been reported [13,14,21]. Patients with decreased numbers of CD4+ T cells showed inferior OS and PFS. A retrospective study of 127 FL patients revealed that low ACD4Cs were statistically significantly associated with a worse PFS and shorter OS. Evaluation of peripheral blood ACD4Cs could be a useful indicator of outcome in previously untreated FL patients [13]. Similarly, Zhang et al. [14] reported that both low ACD4Cs and CD4/CD8 ratios were associated with unfavorable OS by univariate analysis. Low ACD4Cs were found to be a significant predictor of unfavorable OS in patients with MCL [14]. These data suggest that immune factors may play an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of these lymphomas.
In most previous ENKTL studies, the focus has been on nonimmune factors. The prognostic models IPI, KPI, and PINK, including factors such as age, stage, LDH, B symptoms, PS, lymph nodes, and non-nasal and extranodal involvement are the most common models and mainly refer to the patient’s status and the range of tumor involvement [5,6,22]. Two studies concerning the role of the tumor microenvironment in disease progression of ENKTL have found that tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte subsets are important prognostic markers in ENKTL patients. Peng et al. [7] concluded that higher number of CD4+ TILs, especially CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells, was associated with better OS and PFS. In addition, Kim et al. [23] investigated the tumor microenvironment including Treg cells in 64 ENKTL cases. They found that patients with increased numbers of Treg cells showed prolonged OS and PFS by multivariate analysis, which was consistent with Peng et al.’s conclusion [7] that an increased quantity of tumor-infiltrating Treg cells was predictive of improved clinical outcomes in ENKTL patients [24]. Thus, CD4+ T cells may play an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of ENKTL.
However, to the best of our knowledge, there was no data on specific populations of circulating immune cells associated with clinical features and survival outcomes in ENKTL. In ENKTL, previous studies of circulating immune cells mainly focused on ALCs, which considered ALCs as a predictor of immune status. The decreasing ALCs as an indicator of pre-existing immune suppression is an unfavorable prognostic index for ENKTL [9,10]. Because of high-level expression of multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein on ENKTL lymphoma cells, pegaspargase-based therapies were given to untreated ENKTL patients in this study. Our findings revealed that an ACD4C < 0.30×109/L was associated with adverse clinical characteristics and decreased survival, while there was no correlation between ACD8Cs and survival. Moreover, ACD4Cs were found to be an independent prognostic factor for both OS and PFS in multivariate regression analysis that included age, stage, distant lymph nodes, extranasal involvement and ACD4Cs. In the study of Kwong et al. [8], the immune checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab was shown to reactivate effector T cells inducing T cell cytotoxicity in lymphoma cells, and has been shown to be efficacious in the treatment of relapse/refractory ENKTL patients. Some cases showed predominant CD3+CD4+ and CD3+CD8+ T cells infiltrating into residual CD56+EBER+ tumor cells, in which patients finally achieved metabolic complete remission [8].
In the present study, we demonstrated that decreasing ACD4Cs were associated with shorter survival in patients. Low ACD4Cs, predictive biomarker of inferior survival in ENKTL patients, may be associated with the role that CD4+ T cells play in ENKTL. To our knowledge, ENKTL is an EBV-positive tumor related closely to immune functions [25]. The main types of antitumor immune cells are CD4+ and CD8+ T and NK cells. Because NK and CD8+ T cells can be neoplastic cells in ENKTL, CD4+ T cells as non-neoplastic immune cells may play an important antitumor role. Recent findings have shown that CD4+ T cells comprise traditional T helper 1 (TH1), T helper 2 (TH2), Treg, and T helper 17 (TH17) cells, each of them having a significant effect on the pathogenesis of cancers. CD4+ T cells, especially TH1 cells, are the principal immune weapons against tumors. Meanwhile, CD4+ T cells can inhibit tumor progression via the production of tumor necrosis factor, interferon (IFN), and interleukin (IL)-2. Moreover, CD4+ T cells can also enhance CD8+ T cell–mediated antitumor immunity by recruiting activated CD8+ T cells to the tumor through IFN and promoting CD8+ T cell proliferation and cytotoxic function through IL-2 [26,27]. Thus, downregulation of the quantity and quality of CD4+ T cells is an obstacle to antitumor immunity and limits the ability of CD4+ T cells to control and eliminate the tumor.
This study has some limitations. The role of CD4+ T cells in ENKTL has not been sufficiently explored. With the aim of further understanding the role of CD4+ T cells in ENKTL patients, studies that investigate populations of CD4+ T cells such as TH1, TH2, and Treg cells will be needed to confirm the interactions of T cell subsets with tumor cells of ENKTL. In addition, because host immunity undergoes constant changes during treatment, peripheral T cell subsets during and after chemotherapy should be analyzed.
In conclusion, host immunity plays a role in lymphoma progression, the analysis of which may provide useful information for assessing prognosis. This retrospective study has demonstrated that ACD4Cs could be an important predictor of survival in ENKTL. It is possible that immune cells may affect disease progression and may be important therapeutic targets in ENKTL.
AcknowledgmentsWe would like to thank all the treating physicians and all the patients for completing this work. This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81370657, 81470328, 81600130, 81770166, 81720108002), Jiangsu Province’s Medical Elite Programme (ZDRCA2016022), Project of National Key Clinical Specialty, National Science & Technology Pillar Program (2014BAI-09B12), Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Medical Science (BL2014086 and BE2017751) and National Science and Technology Major Project (2017ZX09304032). We thank Mark Abramovitz, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Fig. 1.Overall survival (OS) of 70 patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL). OS of 70 patients with ENKTL, according to the absolute counts of T cell subsets (ACD4Cs) at the time of diagnosis, using Kaplan-Meier estimations. 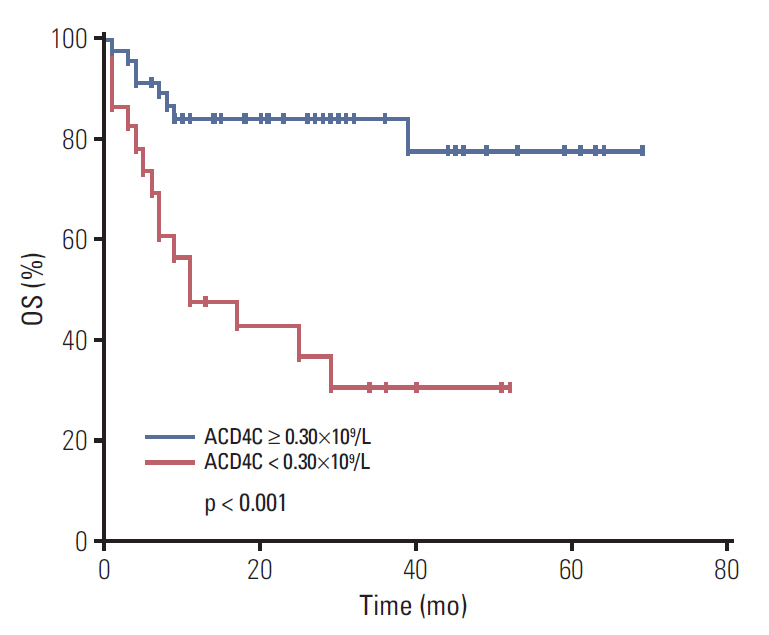
Fig. 2.Progression-free survival (PFS) of 70 patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL). PFS of 70 patients with ENKTL, according to the absolute counts of T cell subsets (ACD4Cs) at the time of diagnosis, using Kaplan-Meier estimations. 
Fig. 3.Survivals of 41 early stage extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL) patients. Survivals of 41 early stage ENKTL patients, according to the absolute counts of T cell subsets (ACD4Cs) at the time of diagnosis. (A) Overall survival. (B) Progression-free survival. 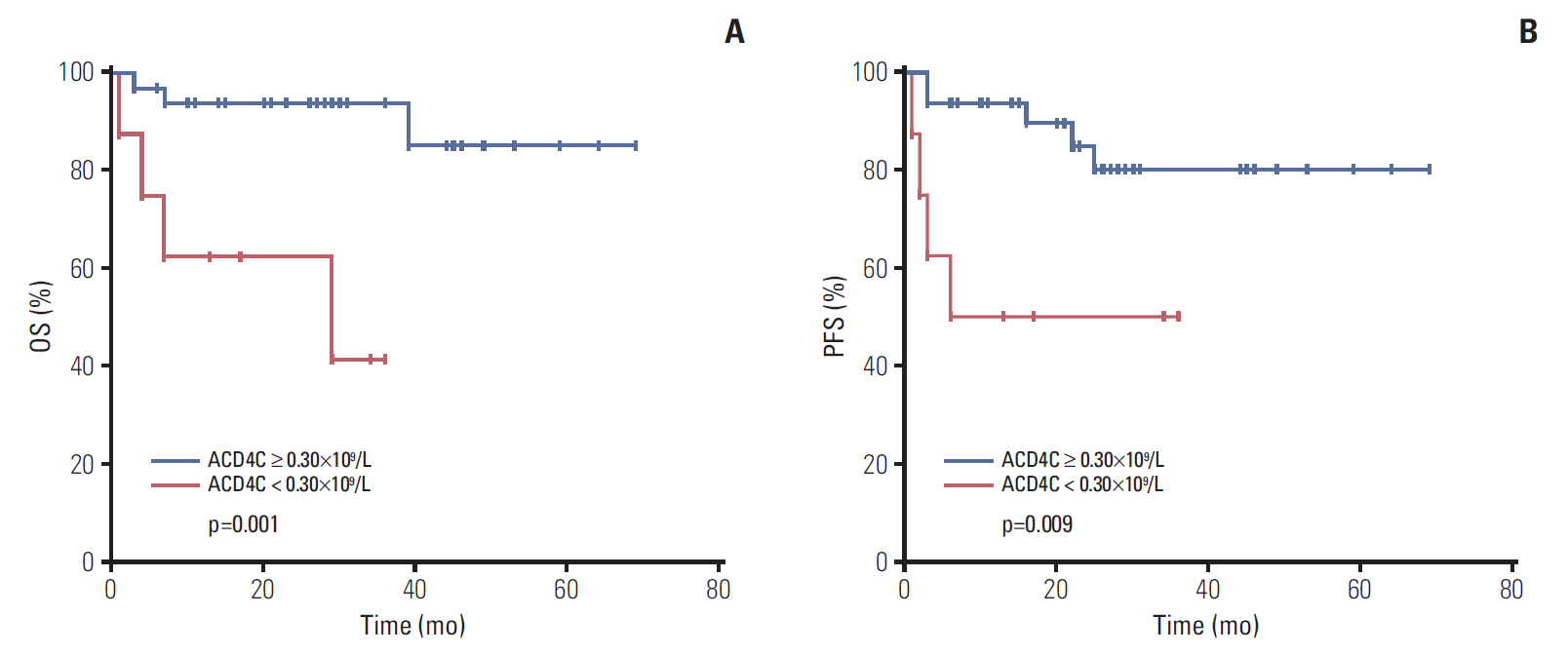
Fig. 4.Survivals of 29 advanced stage extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL) patients. Survivals of 29 advanced stage ENKTL patients, according to the absolute counts of T cell subsets (ACD4Cs) at the time of diagnosis. (A) Overall survival. (B) Progression-free survival. 
Table 1.The clinical characteristics of 70 patients with ENKTL, and associations between of ACD4Cs and characteristics ENKTL, extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type; ACD4Cs, absolute CD4+ T cell counts; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; LN, lymph nodes; IPI, International Prognostic Index; L, low risk; LI, low-intermediate risk; I, intermediate risk; H, high risk; HI, intermediate-high risk; KPI, Korean Prognostic Index; PINK, prognostic index of natural killer lymphoma; ALCs, absolute lymphocyte counts. Table 2.Univariate analyses of prognostic factors for OS and PFS in ENKTL OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; ENKTL, extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; LN, lymph nodes; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; IPI, International Prognostic Index; HI/H, intermediate-high and high risk; KPI, Korean Prognostic Index; PINK, Prognostic Index of Natural Killer Lymphoma; ACD4Cs, absolute CD4+ T cell counts; ACD8Cs, absolute CD8+ T cell counts; ALCs, absolute lymphocyte counts. Table 3.Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors for OS and PFS in ENKTL References1. Yang QP, Zhang WY, Yu JB, Zhao S, Xu H, Wang WY, et al. Subtype distribution of lymphomas in Southwest China: analysis of 6,382 cases using WHO classification in a single institution. Diagn Pathol. 2011;6:77.
2. Xu W, Fan L, Miao Y, Xu H, Yu L, Xu X, et al. Distribution of lymphomas subtypes in Jiangsu Province: a multicenter analysis of 5 147 cases. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014;35:300–3.
3. Au WY, Weisenburger DD, Intragumtornchai T, Nakamura S, Kim WS, Sng I, et al. Clinical differences between nasal and extranasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a study of 136 cases from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood. 2009;113:3931–7.
4. Perry AM, Diebold J, Nathwani BN, MacLennan KA, Muller-Hermelink HK, Bast M, et al. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the Far East: review of 730 cases from the international non-Hodgkin lymphoma classification project. Ann Hematol. 2016;95:245–51.
5. Lee J, Suh C, Park YH, Ko YH, Bang SM, Lee JH, et al. Extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a prognostic model from a retrospective multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:612–8.
6. Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Jaccard A, Chng WJ, Lim ST, Hong H, et al. A prognostic index for natural killer cell lymphoma after non-anthracycline-based treatment: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:389–400.
7. Peng RJ, Huang ZF, Zhang YL, Yuan ZY, Xia Y, Jiang WQ, et al. Circulating and tumor-infiltrating Foxp3(+) regulatory T cell subset in Chinese patients with extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma. Int J Biol Sci. 2011;7:1027–36.
8. Kwong YL, Chan TS, Tan D, Kim SJ, Poon LM, Mow B, et al. PD1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing l-asparaginase. Blood. 2017;129:2437–42.
9. Huang JJ, Jiang WQ, Lin TY, Huang Y, Xu RH, Huang HQ, et al. Absolute lymphocyte count is a novel prognostic indicator in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:149–55.
10. Wang L, Wang JH, Wu-Xiao ZJ, Xia ZJ, Huang HQ, Lu Y. Lymphopenia during routine follow-up may predict relapse in patients with extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:1747–53.
11. Yang Y, Zhang YJ, Zhu Y, Cao JZ, Yuan ZY, Xu LM, et al. Prognostic nomogram for overall survival in previously untreated patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a multicenter study. Leukemia. 2015;29:1571–7.
12. Suzuki R, Suzumiya J, Yamaguchi M, Nakamura S, Kameoka J, Kojima H, et al. Prognostic factors for mature natural killer (NK) cell neoplasms: aggressive NK cell leukemia and extranodal NK cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:1032–40.
13. He L, Liang JH, Wu JZ, Li Y, Qin SC, Miao Y, et al. Low absolute CD4(+) T cell counts in peripheral blood are associated with inferior survival in follicular lymphoma. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:12589–95.
14. Zhang XY, Xu J, Zhu HY, Wang Y, Wang L, Fan L, et al. Negative prognostic impact of low absolute CD4(+) T cell counts in peripheral blood in mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:1471–6.
15. Sabattini E, Bacci F, Sagramoso C, Pileri SA. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues in 2008: an overview. Pathologica. 2010;102:83–7.
16. Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL. X-tile: a new bioinformatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7252–9.
17. Gaulard P, de Leval L. The microenvironment in T-cell lymphomas: emerging themes. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;24:49–60.
18. Coupland SE. The challenge of the microenvironment in B-cell lymphomas. Histopathology. 2011;58:69–80.
19. Blaker YN, Spetalen S, Brodtkorb M, Lingjaerde OC, Beiske K, Ostenstad B, et al. The tumour microenvironment influences survival and time to transformation in follicular lymphoma in the rituximab era. Br J Haematol. 2016;175:102–14.
20. Wein F, Kuppers R. The role of T cells in the microenvironment of Hodgkin lymphoma. J Leukoc Biol. 2016;99:45–50.
21. Chang C, Wu SY, Kang YW, Lin KP, Chen TY, Medeiros LJ, et al. High levels of regulatory T cells in blood are a poor prognostic factor in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2015;144:935–44.
22. Chim CS, Ma SY, Au WY, Choy C, Lie AK, Liang R, et al. Primary nasal natural killer cell lymphoma: long-term treatment outcome and relationship with the International Prognostic Index. Blood. 2004;103:216–21.
23. Kim WY, Jeon YK, Kim TM, Kim JE, Kim YA, Lee SH, et al. Increased quantity of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3-positive regulatory T cells is an independent predictor for improved clinical outcome in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:1688–96.
24. Salama P, Phillips M, Grieu F, Morris M, Zeps N, Joseph D, et al. Tumor-infiltrating FOXP3+ T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:186–92.
25. Hsieh PP, Tung CL, Chan AB, Liao JB, Wang JS, Tseng HH, et al. EBV viral load in tumor tissue is an important prognostic indicator for nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;128:579–84.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||