AbstractPurposeThis retrospective study was carried out to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of radiation therapy (RT) with/without cisplatin-based chemotherapy in nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC).
Materials and MethodsOne hundred forty six patients with NPC received curative RT and/or cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Thirty-nine patients were treated with induction chemotherapy (IC), including cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil followed by RT. Another 63 patients were treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) using cisplatin, and 22 patients were treated with IC followed by CCRT. The remaining 22 patients were treated with RT alone.
ResultsOne hundred four (80.0%) patients achieved complete response (CR), and 23 (17.7%) patients achieved partial response (PR). The patterns of failure were: locoregional recurrences in 21.2% and distant metastases in 17.1%. Five-year overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) were 50.7% and 45.0%, respectively. Multivariate Cox stepwise regression analysis revealed CR to chemoradiotherapy to be a powerful prognostic factor for OS. CR to chemoradiotherapy and completion of radiation according to the time schedule were favorable prognostic factors for PFS. A comparison of each treatment group (IC → RT vs. CCRT vs. IC → CCRT vs. RT alone) revealed no significant differences in the OS or PFS. However, subgroup analysis showed significant differences in both OS and DFS in favor of the combined chemoradiotherapy group compared with RT alone, for stage IV and T3-4 tumors. Grade 3-4 toxicities were more common in the combined chemoradiotherapy arm, particularly in the CCRT group.
ConclusionsThis study was limited in that it was a retrospective study, much time was required to collect patients, and there were imbalances in the number of patients in each treatment group. Combined chemoradiotherapy remarkably prolonged the OS and PFS in subgroup patients with stage IV or T3-4 NPC.
INTRODUCTIONNasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) can be distinguished from other cancers occurring in the head and neck region with respect to epidemiology, histological features, clinical characteristics, treatment strategies, and response to therapy (1). NPC is a relatively rare tumor in Western countries, but it is much more common in Southeast Asian, North African, and Eskimo patients. It is a geographically endemic, Epstein-Barr virus-associated carcinoma of epidermoid origin (2). The tumor tissue of NPC is composed mainly of poorly differentiated or undifferentiated cells with high incidence of lymphatic and hematogenous dissemination. These tumors have a high sensitivity to radiation and chemotherapy. Because of its anatomic limitation for surgical approach and high radiosensitivity, the traditional approach has been to treat this tumor with radiation therapy (RT) rather than with surgery. Although early-stage NPC is highly radiocurable, the treatment outcomes of locoregionally advanced NPC following RT have been disappointing (3). There is a high incidence of distant metastases and local failure in locoregionally advanced disease, despite good local control after initial RT, leading to a 30~50% 5-year survival rate (4). Over the past two decades, many attempts have been made to improve the efficacy of RT for head and neck cancer patients by incorporating some chemotherapeutic agents (5). Chemotherapy has been used neoadjuvantly, concomitantly with radiation, and after radical radiation (6). Combination treatment with chemotherapy and RT has been investigated, with a view to decreasing the incidence of both distant metastasis and locoregional relapse, and to increase the disease-free and overall survival (7-10). Meta-analysis evaluating the impact of integrating chemotherapy with external beam RT has shown an improvement, albeit modest, in the disease-free and overall survival in the clinical setting (11,12). It is still unclear which type of chemotherapy and standard RT integration will improve clinical outcomes in patients with locoregionally advanced NPC.
This article presents the results of a retrospective analysis that pools the data of almost all patients treated for NPC over the last 15 years in our hospital. Even with the limitations associated with a retrospective analysis, the results are expected to provide a clearer understanding of the anti-tumor efficacy and toxicity of combined-modality treatment compared with RT alone in NPC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS1) PatientsThis study examined patients with biopsy-proven, previously untreated stage I to IV NPC according to the 2002 American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system. Other inclusion criteria were Karnofsky performance status ≥60%; adequate bone marrow, liver, and renal function; and no detectable distant metastasis. Between January 1988 and August 2003, 146 NPC patients received curative RT with or without cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The cut-off date for the analysis was August 2008, and almost all patients had been followed-up for a minimum of 5 years.
All patients underwent fiberoptic nasopharyngoscopy and biopsy for pathologic diagnosis. The pretreatment staging evaluations included a clinical examination of the head and neck, computed tomography (CT) scan and/or magnetic resonance imaging from the skull base to the whole neck, chest radiography, whole body bone scan, abdominal sonography, complete blood count with differential count, and biochemical profile. Thirty-nine patients (26.7%) were treated with induction chemotherapy (IC), which included cisplatin 100 mg/m2 for 1 day and 5-fluorouracil 1 g/m2 for 5 days, followed by RT. Another 63 patients (43.1%) were treated with concurrent chemoradiation (CCRT) using cisplatin 100 mg/m2 at 3-week intervals, and 22 patients (15.1%) were treated with IC followed by CCRT. The remaining 22 patients (15.1%) were treated with RT alone.
2) Radiation therapyPatients were treated with 6-MV photons and electrons. In order to increase reproducibility and accuracy, patients were immobilized in a thermoplastic cast. All patients were treated in the supine position, usually through bilateral parallel-opposed fields to the primary tumor and the upper neck and a single anterior field to the lower neck. A three-field combination technique (bilateral opposed and anterior portals) was used for patients with an anterior extension of the primary tumor. After 45~50 Gy, the primary boost field was changed via bilaterally opposed reduced portals or 3-dimensional conformal therapy. The bulky nodal area was boosted using 6-MV photons or an electron beam of appropriate energy. The total median dose administered was 70.2 Gy/7~8 weeks to the primary tumor and the positive neck region (range: 65.0 to 82.8), 55~60 Gy/5~6 weeks to the high risk clinical target volume (CTV) area, and 45~50 Gy/5~6 weeks to the low risk CTV area. A CT simulator has been used to delineate the target volume since 1995, and the field arrangements were individualized. For most patients, the fractionation was 1.8 Gy/fraction, Monday to Friday.
A similar dose and fractionation of RT was administered in each treatment arm.
3) Chemotherapy(1) Induction chemotherapy (IC)The IC regimen consisted of cisplatin at a dose of 100 mg/m2 on day 1 and 5-fluoruracil (5 F-U) 1 g/m2 for 5 days (on Days 1~5), repeated every 3 weeks, and followed by the same RT or CCRT beginning 3 weeks after the third course of IC.
(2) Concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT)Patients undergoing CCRT were scheduled to receive cisplatin 100 mg/m2 in 1 L of half saline over 2 hours, every 3 weeks during external RT, beginning on the first day of RT. Complete blood counts and blood chemistry were checked before each chemotherapy cycle. Chemotherapy was delayed for 7 days if the absolute neutrophil count was ≤1,500/µl or the platelet count was ≤100,000/µl. Dose modifications were allowed based on nadir blood counts and interim toxicities from preceding cycles.
4) Patient follow-upPatients were evaluated for treatment-related toxicity, tumor response, PFS, and OS. Tumor response and acute toxicity were assessed according to the World Health Organization (WHO) and Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) criteria. All patients were subjected to physical examination and complete blood count during each week of therapy. Liver and renal function tests were checked before each cycle of chemotherapy. After completing the treatment schedule, patients were followed up biweekly until acute toxicity had resolved. They were then evaluated every 1 or 2 months during the first year, every 3 months during the second and third years, and every 6 months thereafter. Neck CT scan or MRI, chest radiography, abdominal sonography, whole body bone scan, complete blood count, and biochemistry tests were performed every 6 months for the first 2 years, and then routinely on an annual basis or at the time of the clinical suggestion of tumor relapse.
5) Response evaluationFour to 12 weeks after completion of all treatments, patients were evaluated for tumor response by nasopharyngoscopy and neck CT scan or MRI. Appropriate biopsy specimens were taken when residual disease was suspected.
A complete response was defined as complete disappearance of locoregional disease, as evidenced by physical examination, endoscopic examination, and CT scan or MRI. A partial response was defined as ≥50% shrinkage of all measurable lesions. The presence of residual mucosal thickening in the nasopharynx with unclear significance was scored as a partial response, even if there was no other evidence of disease.
6) Salvage treatmentFor the patients who had relapse or persistent disease, the most appropriate treatment among surgery, chemotherapy, and re-irradiation was selected according to the opinion of the attending physician. Patients with persistent local disease were given boost external RT using a 3-D conformal technique, intracavitary brachytherapy using an iridium-192 source, or fractionated stereotactic RT (FSRT). Patients with residual neck nodes 3~6 months after completion of all treatment schedules were referred for radical neck dissection.
7) Statistical analysisThe primary endpoints of the study were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). OS was defined as the time from the first day of treatment to the time of death from any cause or to the last follow-up visit. PFS was defined as the time from the first day of treatment to the time of disease progression or to the last follow-up visit. Locoregional recurrence-free survival and distant metastasis-free survival were also evaluated.
The Kaplan-Meier method was used to analyze survival, and the log-rank test was used to compare differences between the treatment groups. The Cox regression model was used to assess the independent prognostic factors for OS and PFS. The prognostic factors considered in the Cox model included AJCC stage, T stage, N stage, WHO classification, treatment method, response to chemoradiation, time required to complete RT, and cycles of chemotherapy. Toxicity and tumor response were analyzed using a X2 test. All statistical tests were two-sided, and p-values<0.05 were considered significant. Analyses were performed using the SAS program (Ver. 8.0; SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC).
RESULTS1) Patients Characteristics
Table 1 lists patient baseline characteristics, including age, gender, WHO histological classification, clinical stage (AJCC), and T and N stage.
2) Survival AnalysisAfter a median follow-up period of 139.2 months (range, 58.8 to 252.3 months), the 5-year OS and PFS rates for all patients were 50.7% and 45.0%, respectively. There were no significant differences among the treatment arms. In addition, there were no significant differences in the 5-year OS and PFS rates between the combined chemoradiation arm and the RT alone arm in the overall comparison (52.4% vs. 40.9% and 45.8% vs. 39.7%, p=0.552 and p=0.896, respectively). The addition of cisplatin-based chemotherapy to RT, either in induction or in concomitant administration, showed increases of 11.5% and 6.1% in the 5-year OS and of PFS rates, respectively. However, there were no statistically significant differences between the groups (Table 2). Subgroup analysis showed significant differences in the OS and PFS in favor of the combined chemoradiation group for stage IV (p=0.009 and p=0.031, respectively) and T3-4 tumors (p=0.008 and p=0.037, respectively) (Fig. 1). For these advanced stage tumors, locoregional recurrence-free survival and distant metastasis-free survival were also analyzed to determine if a meaningful survival benefit might be obtained from combined chemoradiotherapy, based on the better control of locoregional recurrence or decreased distant metastases. Both locoregional recurrence and distant failure were significantly lower in the combined chemoradiation groups compared with the RT alone group.
3) Response rateThe complete response rates in the combined chemoradiation arms and the RT-alone arm, which were evaluated at 1~3 months after the completion of the planned treatment, were 81.1% and 73.7%, respectively (p=0.578) (Table 3). Furthermore, there was no significant difference in the CR rate between the CCRT arm and RT alone arm (83.3% vs 73.7%, respectively, p=0.823). Subgroup analysis showed significant differences in the CR rate in favor of the combined chemoradiation group for T3-4 tumors, compared to RT alone (81.7% vs 50.0%, p=0.050). However, for stage III or IV patients, the CR rate was higher in the combined chemoradiation group, but not to a statistically significant degree (80.5% vs 62.5%, p=0.228).
4) Failure pattern
Table 4 lists the incidence and sites of treatment failure at the last assessment. Treatment failure was indicated by the presence of persistent disease and/or the appearance of new lesions or disease progression. Thirty-one (21.2%) patients failed at locoregional sites, and 25 (17.1%) failed at distant sites. Among them, nine patients (6.2%) had both locoregional and distant failure. Forty-nine (39.5%) patients in the combined chemoradiation arms and seven (31.8%) in the RT alone arm relapsed. There were no remarkable differences in failure patterns between the combined chemoradiation arms and the RT alone arm in the overall comparison. During the follow-up period, a second primary cancer developed in six patients: three head and neck cancers, two lung cancers, and one cervical cancer. All patients were successfully salvaged with surgery and/or chemo-irradiation.
5) Patient complianceAlthough acute toxicities (including mucositis, leukopenia, and emesis) were more frequent and severe in the combined chemoradiotherapy arms, particularly the CCRT arm, patient compliance with chemotherapy was relatively good in the combined treatment arms. Fifty-six patients (66.7%) were able to successfully complete the planned three courses of cisplatin chemotherapy in the CCRT arm (n=85), and 76 patients (90.5%) completed two or more courses of cisplatin. There were eight patients in whom the second cycle of cisplatin could not be administered. The reasons for withdrawal of cisplatin included patient's refusal, severe mucositis, prolonged severe neutropenia, and cisplatin-induced renal toxicity. RT was interrupted for more than two weeks in 62 patients (42.5%). This was frequently noted in the combined chemoradiotherapy arms. In the combined chemoradiotherapy arms, 44.4% (55/124) of patients could complete RT within 9 weeks, compared with 63.6% (14/22) of patients in the RT alone arm. An RT interruption of ≥ one week occurred in 46 patients (54.1%) in the CCRT arm and in 23 patients (59.0%) in the IC followed by RT arm. The median duration of RT was 66 days in the combined chemoradiation arm and 58 days in the RT alone arm.
6) Toxicity
Table 5 lists the acute toxicities assessed according to the WHO/RTOG criteria. Grade 3~4 acute toxicities, including hematologic toxicities, mucositis, nausea/vomiting, and anorexia, were more common in the combined chemoradiation group. Grade 3~4 hematologic toxicities (28%) and mucositis (38%) were observed more frequently, particularly in the CCRT arm. Severe cisplatin-induced renal toxicity was noted in three patients in the combined chemoradiation group.
There were four treatment-related deaths: two patients died from sepsis that occurred immediately after administration of cisplatin in the CCRT arm; one patient died from brain necrosis 7.3 years after the completion of radiation; and one patient died from airway obstruction due to progressive flexion contracture of the cervical spine. He had undergone radical neck dissection for residual neck nodes, even after receiving the full dose of RT. One patient developed fibrosarcoma in the irradiated neck 15 years after RT and was successfully salvaged with surgery.
7) Prognostic factors
Table 6 lists the prognostic factors exhibiting a significant correlation with OS and PFS, according to the univariate Log-rank test. Clinical stage (AJCC), T stage, N stage, and tumor response to chemoradiation were found to be significant prognostic factors for OS (p<0.05). The tumor response to chemoradiation, T stage, and duration of RT were prognostic factors for PFS (p<0.05). Multivariate Cox stepwise regression analysis revealed complete response (CR) to chemoradiation to be a powerful prognostic factor for OS (p=0.0001, HR 2.55, 95% CI 1.64~3.75) (Fig. 2). CR to chemoradiation (p=0.0001, HR 2.22, 95% CI 1.36~3.04) and completion of the planned radiation schedule (p=0.008, HR 2.07, 95% CI 1.63~3.63) were also favorable prognostic factors for PFS (Fig. 3).
Although a slight increase in the OS and PFS rates were observed in patients receiving more than three cycles of cisplatin in the CCRT arm, there were no statistically significant differences between those patients receiving one or two cycles of cisplatin (p=0.364 and p=0.165, respectively).
DISCUSSIONNPC is highly sensitive to chemotherapy, particularly cisplatin-based regimens (13). Recently, considerable attention has been focused on combinations of RT and chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced NPC. However, there is some controversy regarding the choice of chemotherapeutic agent, the timing of delivery and dosage, and the duration of therapy (3). In general, three different strategies have been used to incorporate chemotherapy into the standard course of RT: before (neoadjuvant); during (concurrent); and after (adjuvant) RT (3). Each modality of combined treatment regimens has both advantages and disadvantages, and has been studied extensively over the last two decades.
There have been several phase III randomized trials aimed at examining the role of combined chemoradiotherapy in NPC (5,7-10,14-15). Unfortunately, most studies of neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy have reported no survival benefit. The most important clinical trial has been the US Intergroup study (14), which was the first randomized trial to show a survival benefit with CCRT followed by adjuvant chemotherapy. However, its application to non-American NPC patients is controversial considering the differences in racial composition and the distribution of pathologic subtypes, as well as the unexpected inferior results in the RT alone group, which was used as the control arm (3). Because different staging systems, prognostic factors, chemotherapeutic drugs, and treatment schedules have been used in previous studies, it is very difficult to compare these studies without partiality and to determine the optimal treatment (3).
Lin et al. re-examined why most phase III randomized trials of combination treatment failed to demonstrate significant survival benefit with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (3). They suggested possible reasons, including the relatively low dose of cisplatin (120 to 180 mg/m2) used in the Asian-Oceanian Clinical Oncology Association trial (10), the excess of severe treatment-related toxicities, refusal of RT in the International Nasopharynx Cancer Study Group trial (9), and inclusion of patients with less advanced stage of NPC (10).
Indeed, subgroup analysis of the patients with bulky neck lymph nodes >6 cm in the Asian-Oceanian Clinical Oncology Association trial showed that neoadjuvant chemotherapy improved the 3-year relapse-free survival (63% vs. 28%, p=0.026) and OS (73% vs. 37%, p=0.057) (10). Similar findings were obtained in the present study. There were no statistically significant differences in the OS or PFS between the treatment arms after a median follow-up period of 139.2 months. Subgroup analysis demonstrated a clear benefit in OS and PFS, in favor of the combined chemoradiotherapy arm in the advanced T3-4 stage and stage IV. However, there was no significant survival advantage in stages I~III. It is believed that the survival benefit in this subgroup of advanced NPC might come from reduced distant metastasis and might be improved by locoregional control. This suggests that advanced stage NPC might benefit from aggressive CCRT. The failure to demonstrate a significant survival advantage in early stage NPC patients indicates that aggressive RT alone could achieve comparable clinical outcomes with CCRT. An additional survival benefit could not be expected for early stage NPC, even when chemotherapy was combined with RT. This was both attributable to effective locoregional control by RT only and to fewer occurrences of distant metastasis. Another possible explanation for the lack of survival benefit in the CCRT arm is the dose and schedule of cisplatin administration. The 3-week schedule of high dose cisplatin in this study, which was associated with a high incidence of acute treatment-related toxicities and prolonged courses of radiation, might have resulted in suboptimal benefit in the CCRT arm. Univariate log rank tests and multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that completion of radiation according to the time schedule was one of the favorable prognostic factors for PFS. In the CCRT arm, only 45.9% of patients could complete RT with a delay of less than 1 week (within 9 weeks), compared with 63.6% in the RT alone arm. It appears that prolongation of the radiation course was a major cause of suboptimal outcomes in the CCRT arm.
Meta-analysis of CCRT in locally advanced head and neck cancer showed that survival benefit mainly originated from the enhancing effects of chemotherapy to radiation on the primary tumor (11,12).
In this study, 56 of 85 CCRT patients (66.7%) successfully completed the planned three courses of cisplatin. Patient compliance was comparable to that seen in the Intergroup-0099 study (14), in which 63% of the patients completed the planned treatment schedule, including three courses of concurrent cisplatin (100 mg/m2). However, in the phase III trial conducted by Lin et al., 132 of 141 patients (93.6%) completed their planned CCRT schedule (3). These two clinical studies demonstrated a significant survival gain with respect to OS and PFS, favoring the CCRT arm. Lin et al. (3) reported that their CCRT protocol had induced a much lower frequency of severe leukopenia (4.3%) and emesis (4.3%), which differs from the findings of the Intergroup trial (29.5% and 14.1%, respectively) (14). It is believed that the lower incidence of acute toxicities and the excellent compliance seen in Lin's study might have arisen from different doses, regimens, and chemotherapy schedules. Their chemotherapy schedule consisted of cisplatin 20 mg/m2/day with 5-FU 400 mg/m2/day as a 96-hour, continuous infusion during the first and fifth weeks of RT.
When cisplatin is combined with RT, it acts both as a cytotoxic agent and as a radiation sensitizer. The optimal combination schedule of cisplatin and radiation has not yet been established. Daily low-dose, weekly intermediate-dose, and 3-week high-dose cisplatin regimens have been used (5).
Concern has been raised about serious acute toxicity, which is inevitably induced when 3-week high dose cisplatin is combined with aggressive RT in Oriental patients. There is only limited evidence to support the use of CCRT for NPC patients in endemic areas in Southeast Asia (16-18). Nevertheless, encouraging results have been reported from several clinical studies using a weekly moderate dose of cisplatin administered concomitantly with RT (19). We have recently tried an intermediate dose of weekly cisplatin (30 mg/m2) concurrently with RT in an attempt to increase the radiation enhancing effect of cisplatin and to enhance patient compliance. Our preliminary results showed that a weekly intermediate dose of cisplatin (30 mg/m2) is practical and feasible for CCRT treatment of NPC, with regard to decreasing interruptions in radiation treatment and minimizing acute toxicities, without compromising local control (20).
In advanced NPC, the pattern of treatment failure is characterized by a high incidence of local recurrence and distant metastasis. Some reports have shown distant metastases to be the main manifestation of treatment failure (21,22), but local recurrences have outnumbered distant failures in other reports (23). In this study, 21.2% of patients had locoregional failure and 17.1% had distant failure. Regardless of the major sites of failure, locoregional control is most important in NPC patients with clinically localized disease and no distant metastases. In other words, if locoregional control cannot be achieved, it is impossible to expect long-term survival in NPC. Frequently, locoregional recurrences in NPC patients are followed by subsequent distant metastases (24). Therefore, 3-dimensional conformal RT and intensity-modulated RT have become popular treatment modalities for improving locoregional control of advanced NPC. Stereotactic radiosurgery has been applied as a boost tool for residual tumors, even after conventional RT has been performed.
The Intergroup study employed a treatment schedule including an additional three courses of adjuvant chemotherapy after CCRT, in order to further reduce the incidence of distant treatment failure (14). This strategy could be easily incorporated into the current CCRT protocol, but the survival benefit needs to be confirmed by large-scale, prospective, randomized trials.
A recent meta-analysis (25) looking at fourteen randomized clinical trials of chemotherapy in NPC demonstrated that the addition of chemotherapy to radiation had a small but significant effect on OS (HR 0.83, 95% CI: 0.76~0.95; p<0.0001). The largest effect was noted in CCRT, which corresponded to a 34% decrease in the risk of death (HR 0.64, 95% CI: 0.50~0.82). No significant OS benefit was noted with neoadjuvant chemotherapy or adjuvant chemotherapy. This data provides further evidence that adjuvant chemotherapy does not appear to improve treatment results. Hence, CCRT followed by adjuvant chemotherapy, which is commonly practiced in the U.S., needs to be confirmed by a larger number of prospective trials. Furthermore, active clinical research for more effective neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by CCRT is warranted. Clearly, there is a need for further randomized clinical trials to address the integration of chemotherapy and radiation in this disease.
CONCLUSIONAlthough our data did not show an additional survival benefit with combined chemoradiation compared to RT alone, combined chemoradiation clearly produced significant prolongation in OS and PFS, particularly in patients with stage IV and T3-4, advanced NPC. Since the systemic and local toxicities were generally acceptable and manageable, concurrent chemoradiation could be recommended as a current standard treatment for locoregionally advanced NPC.
Because this study had several limitations-its retrospective nature, the extended period required to collect patients, and the imbalance in the number of patient in each treatment group-the clinical benefit of combined chemoradiation including CCRT for advanced NPC could not be fully determined. Therefore, further prospective randomized clinical trials are needed.
NotesThe preliminary results of this study were presented at the 2005 annual meeting of the European Society of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology. References1. Altun M, Fandi A, Dupuis O, Cvitkovic E, Krajina Z, Eschwege F. Undifferentiated nasopharyngeal cancer (UCNT): Current diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;32:859–877. PMID: 7790274
2. Ho JH. An epidemiologic and clinical study of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1978;4:182–189. PMID: 640889
3. Lin JC, Jan JS, Hsu CY, Liang WM, Jiang RS, Wanh WY. Phase III study of concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: positive effect on overall and progression free survival. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:631–637. PMID: 12586799
4. Teo P, Yu P, Lee WY, Leung SF, Kwan WH, Yu KH, et al. Significant prognosticators after primary radiotherapy in 903 nondisseminated nasopharyngeal carcinoma evaluated by computer tomography. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;36:291–304. PMID: 8892451
5. Chan AT, Teo PM, Ngan RK, Leung TW, Lau WH, Zee B, et al. Concurrent chemotherapy-radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: progression-free survival analysis of phase III randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:2038–2044. PMID: 11956263
6. Ali H, Al-Sarraf M. Chemotherapy in advanced nasopharyngeal cancer. Oncology. 2000;14:1223–1230. PMID: 10989829
7. Chan AT, Teo PM, Leung TW, Leung SF, Lee WY, Yeo W, et al. A prospective randomized study of chemotherapy adjunctive to definitive radiotherapy in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;33:569–577. PMID: 7558945
8. Rossi A, Molinari R, Boracchi P, Del Vecchio M, Marubini E, Nava M, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy with vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin after radiotherapy in local-regional nasopharyngeal cancer: Results of a 4-year multicenter randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 1988;6:1401–1410. PMID: 3047335
9. International Nasopharynx Cancer Study GroupPreliminary results of a randomized trial comparing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (cisplatin, epirubicin, bleomycin) plus radiotherapy vs. radiotherapy alone in stage IV (≥N2, M0) undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A positive effect on progression-free survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;35:463–469. PMID: 8655368
10. Chua DT, Sham JS, Choy D, Lorvidhaya V, Sumitsawan Y, Thongprasert S, et al. Preliminary report of the Asian-Oceanian Clinical Oncology Association randomized trial comparing cisplatin and epirubicin followed by radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in the treatment of patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 1998;83:2270–2283. PMID: 9840526
11. Huncharek M, Kupelnick B. Combined chemoradiation versus radiation therapy alone in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: results of a meta-analysis of 1,528 patients from six randomized trials. Am J Clin Oncol. 2002;25:219–223. PMID: 12040275
12. Baujat B, Audry H, Bourhis J, Chan AT, Onat H, Chua DT, et al. Chemotherapy in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An individual patient data meta-analysis of eight randomized trials and 1,753 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;64:47–56. PMID: 16377415
13. Boussen H, Cvitkovic E, Wendling JL, Azli N, Bachouchi M, Mahjoubi R, et al. Chemotherapy of metastatic and/or recurrent undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma with cisplatin, bleomycin, and fluorouracil. J Clin Oncol. 1991;9:1675–1681. PMID: 1714951
14. Al-Sarraf M, LeBlanc M, Giri PGS, Fu KK, Cooper J, Vuong T, et al. Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: Phase III randomized Intergroup Study 0099. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:1310–1317. PMID: 9552031
15. Ma J, Mai HQ, Hong MH, Min HQ, Mao ZD, Cui NJ, et al. Results of a prospective randomized trial comparing neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus radiotherapy with radiotherapy alone in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:1350–1357. PMID: 11230478
16. Tan EH, Chau ET, Wee J, Tan T, Fong KW, Ang PT, et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy in Asian patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: toxicities and preliminary results. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;45:597–601. PMID: 10524411
17. Lee AW, Lau WH, Tung SY, Chua DT, Chappell R, Xu L, et al. Preliminary results of a randomized study on therapeutic gain by concurrent chemotherapy for regionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: NPC-9901 trial by the Hong Kong nasopharyngeal carcinoma study group. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6966–6975. PMID: 16192584
18. Wee J, Tan EH, Tai BC, Wong HB, Leong SS, Tan T, et al. Randomized trial of radiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with AJCC/IUAC stage III and IV nasopharyngeal cancer of the endemic varieties. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6730–6738. PMID: 16170180
19. Bachaud JM, Cohen-Jonathan E, Alzieu C, David JM, Serrano E, Daly-Schveitzer N. Combined postoperative radiotherapy and weekly cisplatin infusion for locally advanced head and neck carcinoma: Final report of a randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;36:999–1004. PMID: 8985019
20. Kim TH, Ko YH, Lee MA, Kim BS, Chung SR, Yoo IR, et al. Treatment outcome of cisplatin-based concurrent chemoradiotherapy in the patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2008;40:62–70.
21. Hsu MM, Tu SM. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwan: Clinical manifestations and results of therapy. Cancer. 1983;52:362–368. PMID: 6190547
22. Lee AW, Poon YF, Foo W, Law SC, Cheung FK, Chan DK, et al. Retrospective analysis of 5037 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated during 1976-1985: Overall survival and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;23:261–270. PMID: 1587745
23. Vikram B, Mishra UB, Strong EW, Manolatos S. Patterns of failure in carcinoma of the nasopharynx: Failure at the primary site. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985;11:1455–1459. PMID: 3926733
24. Kwong D, Sham J, Choy D. The effect of loco-regional control on distant metastatic dissemination in the carcinoma of the nasopharynx: An analysis of 1301 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994;30:1029–1036. PMID: 7961008
25. Langendijk JA, Buter J, Leemans CR. A meta-analysis on the value of chemotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An update. Otorinolaryngologie a Foiatrie, [abstract]. 2006. 55:International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Society; p. 017.
Fig. 1Comparison of OS and PFS in the combined chemoradiotherapy arm (CRT, solid line) versus the radiotherapy alone arm (dashed line) in the T3 and T4 (A) and stage IV (B) subgroups. This figure demonstrates the benefit of CRT with regard to OS and PFS. 
Fig. 2Comparison of OS and PFS in patients who showed complete response to chemoradiotherapy (solid line) versus those who showed partial response to chemoradiotherapy (dashed line). 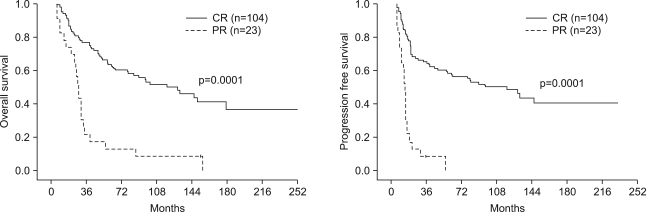
Fig. 3Comparison of PFS in patients in whom RT was not prolonged more than 2 weeks (solid line) versus patients in whom RT was prolonged more than 2 weeks (dashed line). 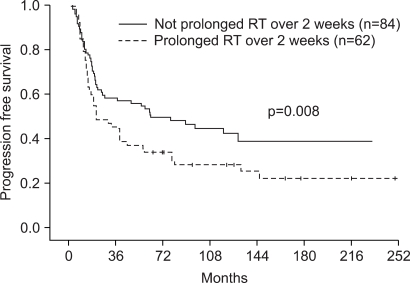
Table 2Treatment outcome according to treatment modality  *five-year overall survival rate, †five-year progression-free survival rate, ‡radiotherapy, §concurrent chemoradiotherapy, ∥Combined chemoradiotherapy includes 3 treatment arms: induction chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy; concurrent chemoradiotherapy; and induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||